Extended Data Fig. 1. UBE2N~UB/UBE2V1/RNF4 RING E3 complex reacts preferentially with free amino acids harboring amine acceptors and various side-chain.
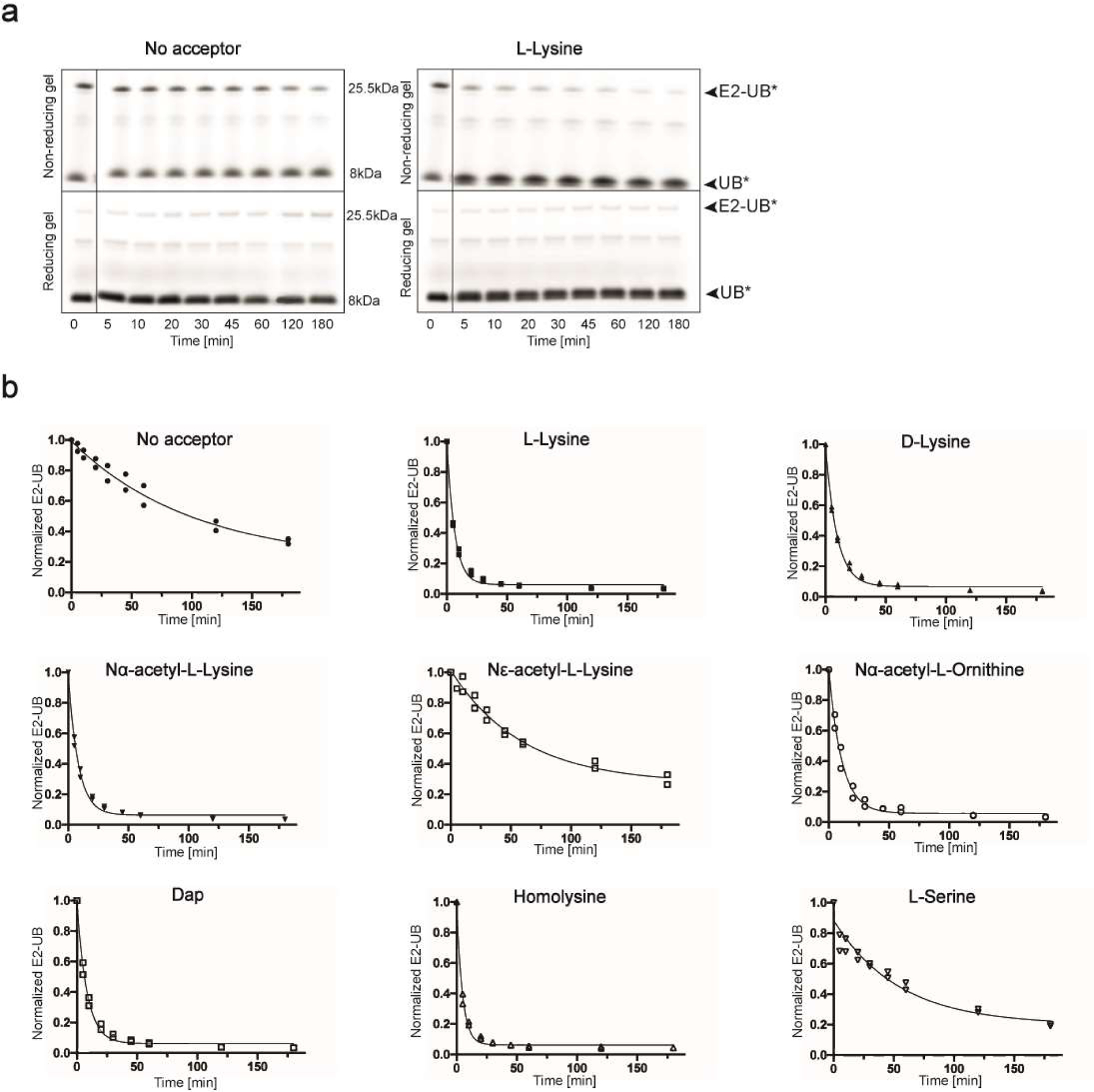
(a) Fluorescence scan of SDS-PAGE gels demonstrating the discharge of labeled UB (UB*) to L-lysine compared with the absence of amino acid acceptor using wild-type UBE2N. Electrophoresis was performed under both reducing and non-reducing conditions to differentiate thioester bonded complexes from isopeptide bonded E2-donor UB ones. (b) Time-courses of fluorescent UB discharge from UBE2N K92R~UB/UBE2V1/RNF4 RING E3 to the indicated amino acids, normalized to starting signal of fluorescent UB thioester-bonded to UBE2N. For all, N=2 independent experiments. For samples derived from the same experiment, gels were processed in parallel.
