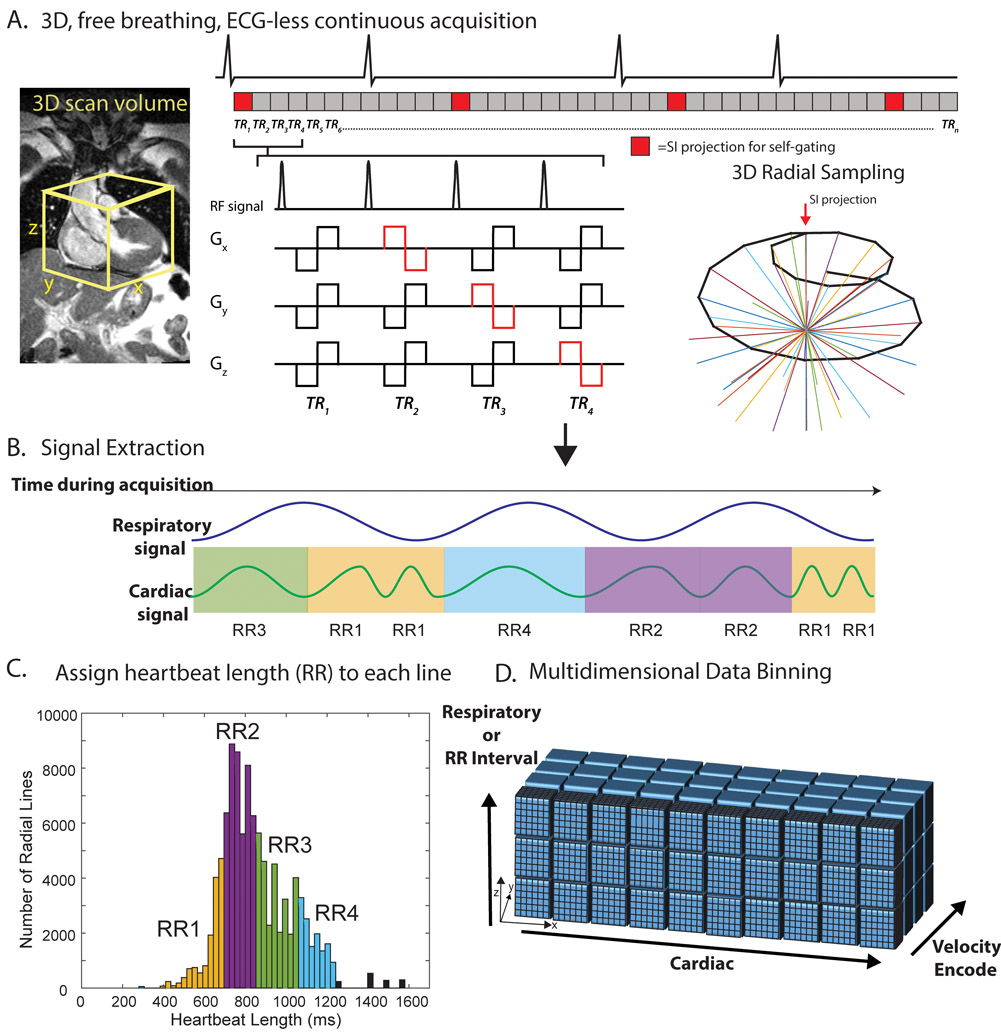
Figure 1: 5D flow RR-binning framework.
A, a transverse, 3D radial imaging volume was placed over the heart. 4-point velocity encoding was combined with a 3D radial, spiral phyllotaxis, sampling pattern. A periodic superior-inferior (SI) projection started each interleaf (red blocks). B, the SI projections were used to extract cardiac and respiratory signals. Each heartbeat was additionally assigned a heartbeat length (RRLength) and binned into one of four RR bins (RR1-RR4). C, histogram of RR intervals for a representative patient colored by bins corresponding to RR bins. Black bars represent outlier heartbeats with that were not included in the binning. D, multidimensional reconstruction. ECG is shown for demonstration purposes only. Actual cardiac and RR binning were done via extracted SI projections. TR=repetition time.