Figure 1: Free PEG and tolerogenic nanoparticles reduce titer of APA induced by PEGylated liposomes.
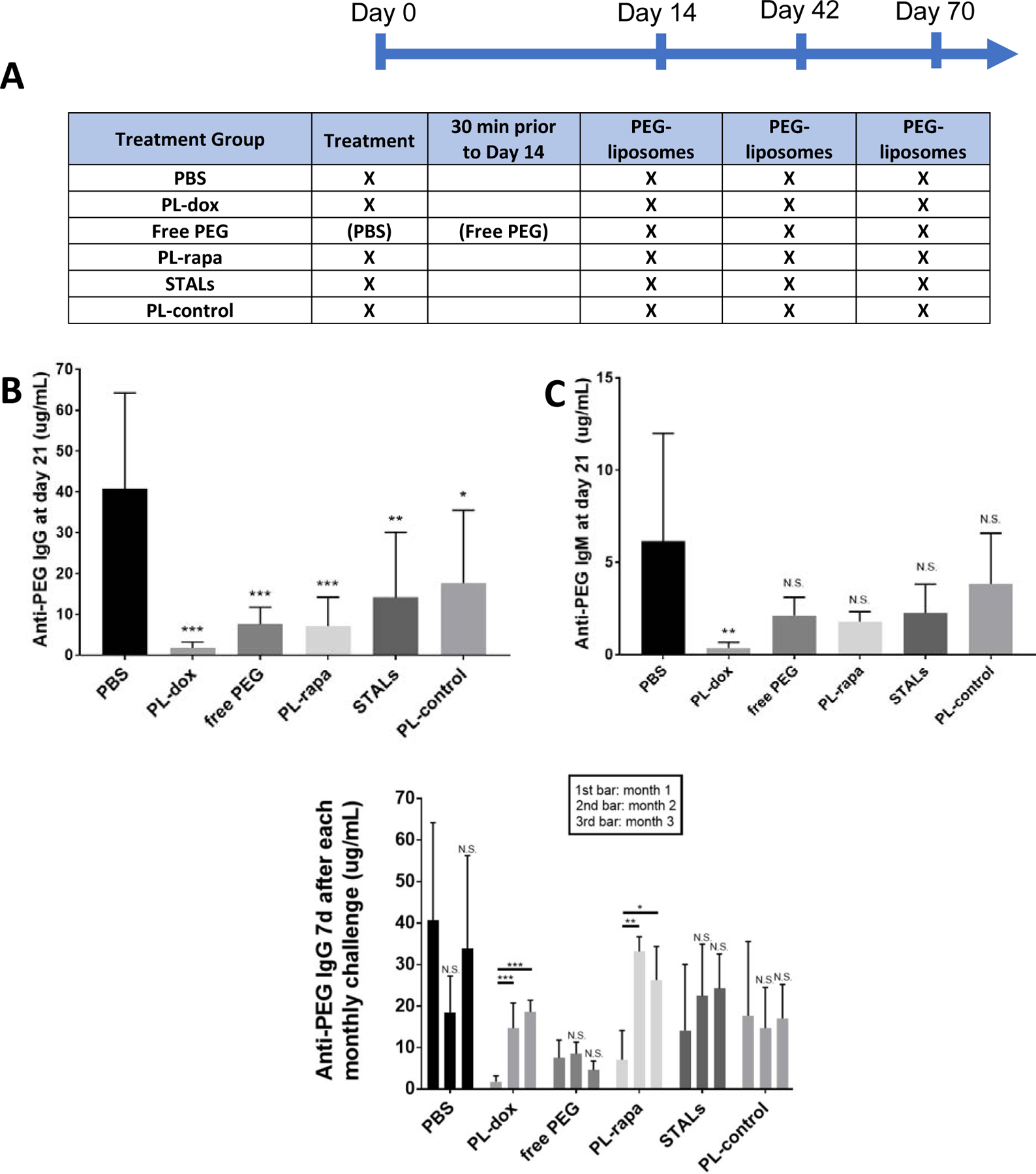
Mice were given an i.v. injection of tolerogenic nanoparticles or PBS on Day 0, prior to i.v. injection of empty PEG-liposomes and NP-Ficoll (a control T-independent antigen) on Day 14. Animals in the free PEG group received PBS at Day 0, and a dose of 40 kDa free PEG 30 minutes prior to the dosing of PEG-liposomes on day 14. PEG-liposomes were also dosed on Day 42 and Day 70. At Day 21, 49 and 77, blood was collected, and the concentrations of anti-PEG IgG and IgM were measured in plasma. (A) Scheme of experimental design, where X indicates specific interventions given. (B) Comparison of anti-PEG IgG produced in mice treated with saline, free PEG, or various tolerogenic particles at Day 21. (C) Comparison of anti-PEG IgM produced in mice treated with saline, free PEG, or various tolerogenic particles at Day 21. Statistical comparisons across groups were T tests and were Bonferroni-adjusted for multiple comparisons. (D) Anti-PEG IgG response 7 days after each of the three PEG-liposome challenges: the first bar is anti-PEG IgG 1 week after first PEG-liposome infusion (Day 21), the second bar is anti-PEG IgG 1 week after second PEG-liposome infusion (Day 49), and the third bar is anti-PEG IgG one week after the third PEG-liposome infusion (Day 77). The experiments in panels B and C were conducted twice, with 4 mice per group, per experiment, for a total of 8 animals per condition. The long-duration studies in panel D (2nd and 3rd challenges) were conducted once, with n=4 per treatment group except for the PBS control group, which had 8 mice. Comparisons across group averages were conducted using unpaired t-tests, with *,**, and *** representing p<0.05, 0.01, and 0.001, respectively.
