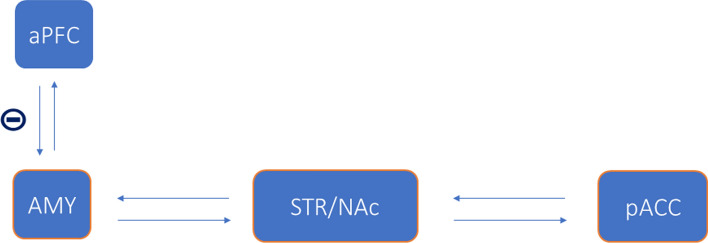
Fig.1.
Neurocircuits associated with social avoidance in the healthy human model. Based on findings that: (1) The aPFC regulates approach-avoidance actions by top-down inhibition of the amygdala. (2) The amygdala has repeatedly been found to be hyperactive in response to social threat, specifically in socially anxious and avoidant participants. (3) The mesolimbic reward circuit is possibly altered in socially anxious participants as indicated by reduced NAc activity in response to social reward. (4) The functional connectivity between the amygdala and NAc, as well as NAc and pACC, alters as a function of social anxiety. aPFC anterior prefrontal cortex, AMY amygdala, STR striatum, NAc nucleus accumbens, pACC perigenual anterior cingulate cortex