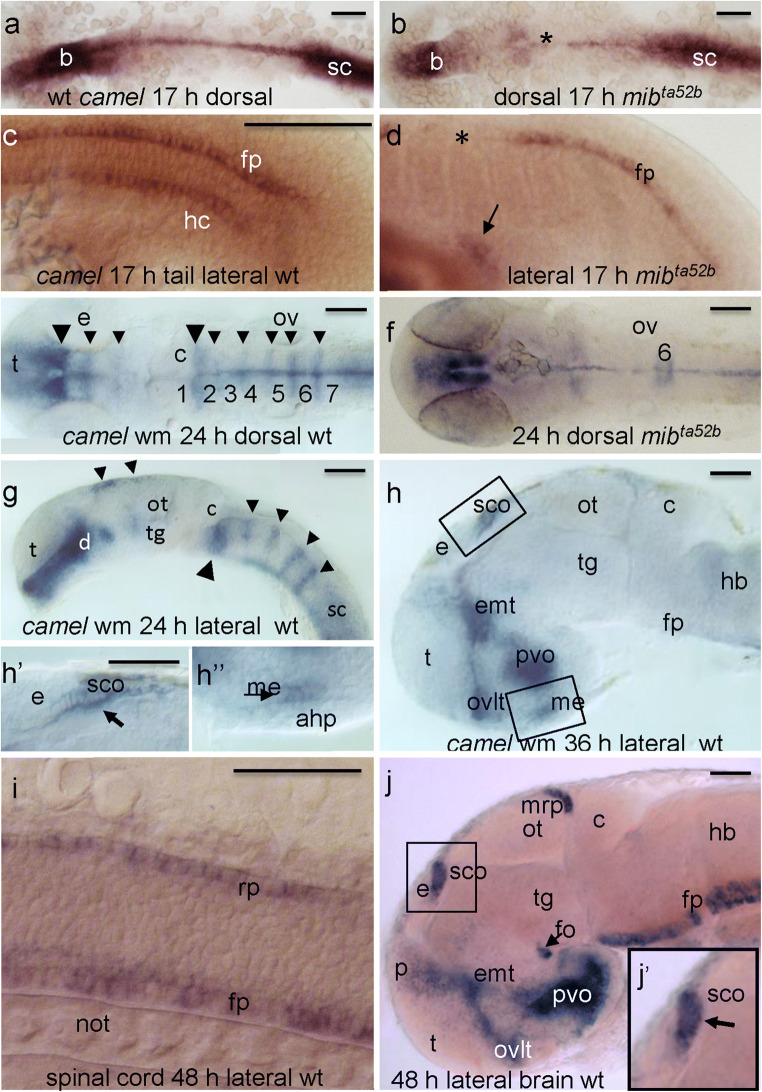
Fig. 3.
The expression pattern of camel in wild-type embryos and mutants detected by whole-mount in situ hybridization during neurogenesis. camel is expressed in the axial structures (fp, rp, hp), along segmental boundaries in the brain and in circumventricular organs. a, c 17 hpf, wild-type embryos. b, d 17 hpf, mibta52b mutant. e, g 24 hpf, wild-type embryos. f 24 hpf, mibta52b mutant. h 36 hpf, brain of a wild-type embryo. i Wild-type trunk, 48 hpf. h, j Wild-type brain, 48 hpf. Numbers define rhombomeres of the hindbrain, asterisk indicates gaps in the floor plate, and arrow indicates remains of hypochord. a, b, e, f Dorsal view. c, d, g–j Lateral view. Abbreviations: ahp, adenohypophysis; b, brain; c, cerebellum; d, diencephalon; e, epiphysis; emp, eminentia thalami; epIII, ependyma of the third ventricle; ey, eye; hb, hindbrain; ht, hypothalamus; fo, flexural organ; fp, floor plate; hb, hindbrain; hc, hypochord; ht, hypothalamus; me, median eminence; mrp, midbrain roof plate; not, notochord; ot, optic tectum; ov, otic vesicle; ovlt, organum vasculosum lamina terminalis; pvo, paraventricular organ; rp, roof plate; sc, spinal cord; sco, subcommissural organ; t, telencephalon; tg, tegmentum. Scale bar = 100 μm