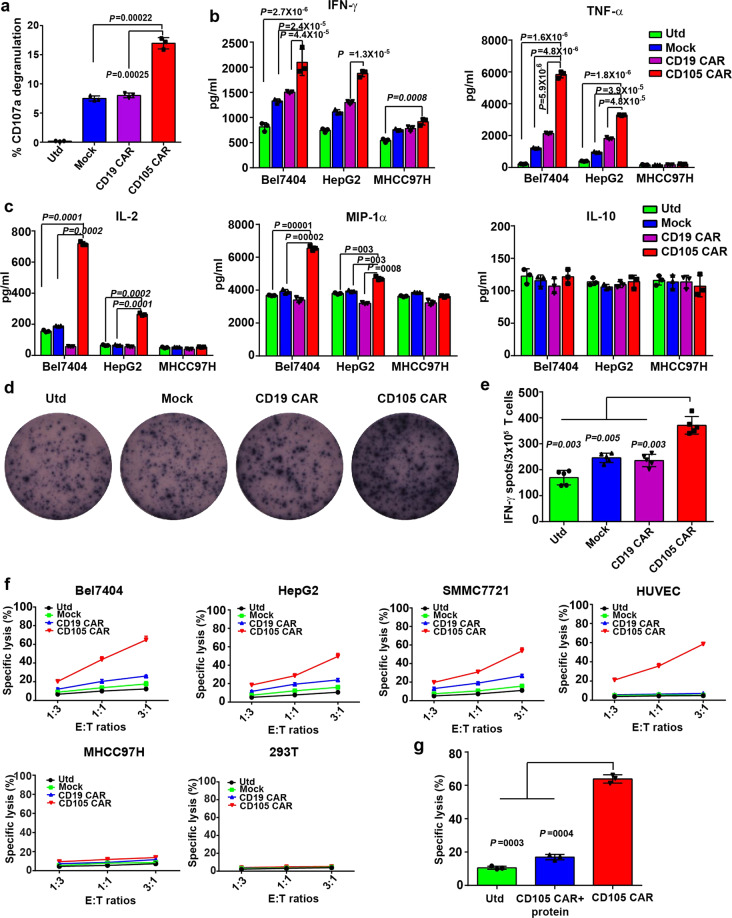
Fig. 4.
Anti-CD105 CAR-T cells express CD107a, secrete positive regulatory cytokines, and efficiently kill CD105-positive cells. a Anti-CD105 CAR-T cells undergo specific degranulation to CD105+ cell. The anti-CD105 CAR, CD19 CAR, Mock, and Utd T cells were incubated with tumor cell for 12 h and CD107a degranulation was measured by flow cytometry. The percentages of CD107a+ T cells of total anti-CD105 CAR-T cells were significantly higher than that of any other groups. b, c Anti-CD105 CAR-T cells produced higher levels of cytokines. CAR-T cells and Utd T cells were incubated with tumor cells for 12 h; the levels of cytokines in the culture supernatants were determined by ELISA assay. d, e ELISPOT analysis of the frequency of IFN-γ-secreted anti-CD105 CAR-T cells. f The anti-CD105 CAR-T cells were co-incubated with the indicated cells labeled with PKH26 at E/T ratio 1 : 3, 1 : 1, and 3 : 1 for 16 h and the ratios of PHK26+PI+ were measured by flow cytometry. Anti-CD105 CAR-T cells had potent cytotoxicity against CD105+ target cell and no cytotoxicity against CD105− target cell. g CD105 CAR-T was incubated with CD105 protein for 30 min and then co-cultured with Bel7404 at an E/T ratio of 3 : 1 by flow cytometry assay. The results show that the killing effect of CD105 CAR-T on target cells is reduced after incubated with CD105 protein, indicating that CD105 CAR-T cells are targeted to CD105-positive cells. Data show the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. The quantitative analysis was used by one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons test