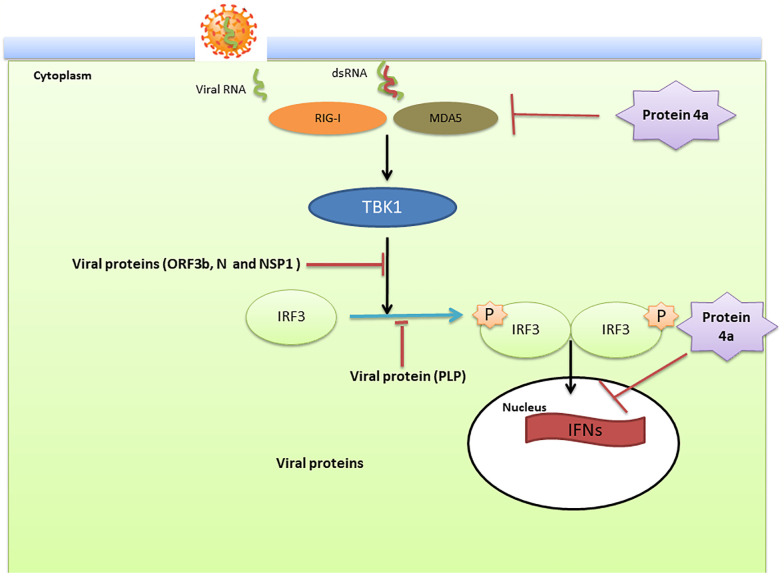
Figure 4.
The innate immune modulation mechanisms by SARS-CoV and Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (MERS-CoV). Double stranded (ds)RNA, a by-product of RNA virus replication in the cytoplasm, is sensed by the pattern recognition receptors such as retinoic-acid inducible gene I (RIG-I) and melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 (MDA5) which subsequently leads to activation of the kinase TANK Binding Kinase 1 (TBK1). These kinases then phosphorylate interferon (IFN) regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) and traffic to the nucleus to active the transcription of IFNs. Viral proteins actively modulate this pathway. Open reading frame (ORF)3b, nucleocapsid (N), and non-structural protein (NSP)1 affect the signal transduction pathway that activates IRF3. In addition, the papain-like protease (PLP) blocks the phosphorylation of IRF3 and its activation. Viral protein 4a suppress the activation of RIG-I/MDA5 signaling and blocks the induction of IFNs through interaction with dsRNA.