Figure 2.
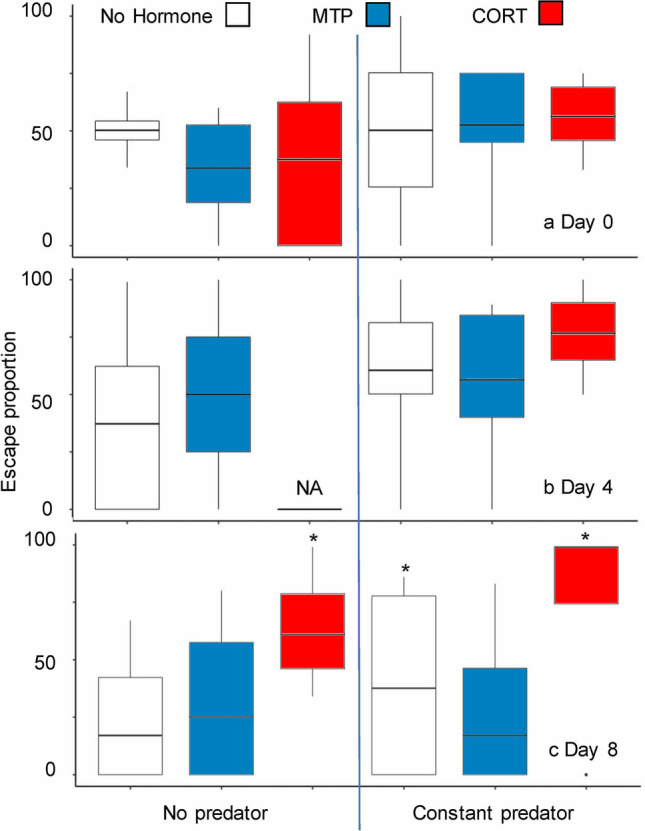
Treatment with corticosterone (CORT) or constant exposure to nonlethal predators increased the ability of wood frog tadpoles to escape predator attack. Shown are boxplots (median and interquartile range) of percentage of Anax attacks from which tadpoles successfully escaped in each treatment combination (n = 4 replicates) on Day 0 (a), Day 4 (b), and Day 8 (c). NA indicates a treatment in which no data were recorded due to technical problems. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared to the No predator/No hormone treatment (P < 0.05).
