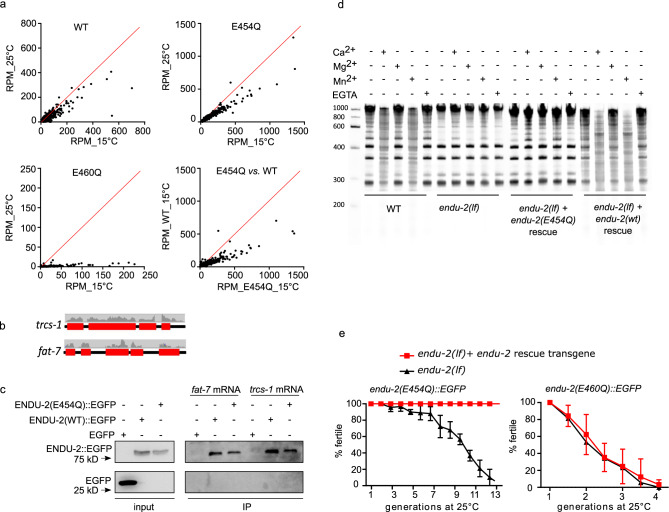
Fig. 4. RNA binding but not RNA-cleavage activity of ENDU-2 protects germline immortality.
a Comparison of RNA binding activities of ENDU-2(wt)::EGFP, ENDU-2(E454Q)::EGFP, and ENDU-2(E460Q)::EGFP at 15 and 25 °C. Shown are plotted normalized reads (RPM) from RIP-Seq of each identified transcript under different conditions. b Mapping of the RIP-Seq reads of two representative binding targets of ENDU-2. Only fragments of mRNA exons (red boxes) but not introns (black lines) were co-immunoprecipitated with ENDU-2. c ENDU-2::EGFP variants bind to selected mRNAs in vitro. Shown are western blots to detect proteins binding to fat-7 and trcs-1 mRNA, respectively. EGFP is a negative control. N = 3 biological replicates. The uncropped blots are included in Supplementary Fig. 11b. d Wild type ENDU-2, but not ENDU-2(E454Q), leads to RNA decay (smear) in a Ca2+ and Mn2+ dependent manner, N = 3. Shown is fused images of two gels from one experiment. The results of additional two biological replicates are shown in Supplementary Fig. 8a. e endu-2(E454Q)::EGFP but not endu-2(E460Q)::EGFP transgene rescues the Mrt phenotype. Data are mean ± SD, N = 3. Both endu-2(tm4977) and endu-2(tm4977) carrying endu-2(E454Q)::EGFP or endu-2(E460Q)::EGFP transgenes were decedents of one single P0 animal carrying the respective transgenes.