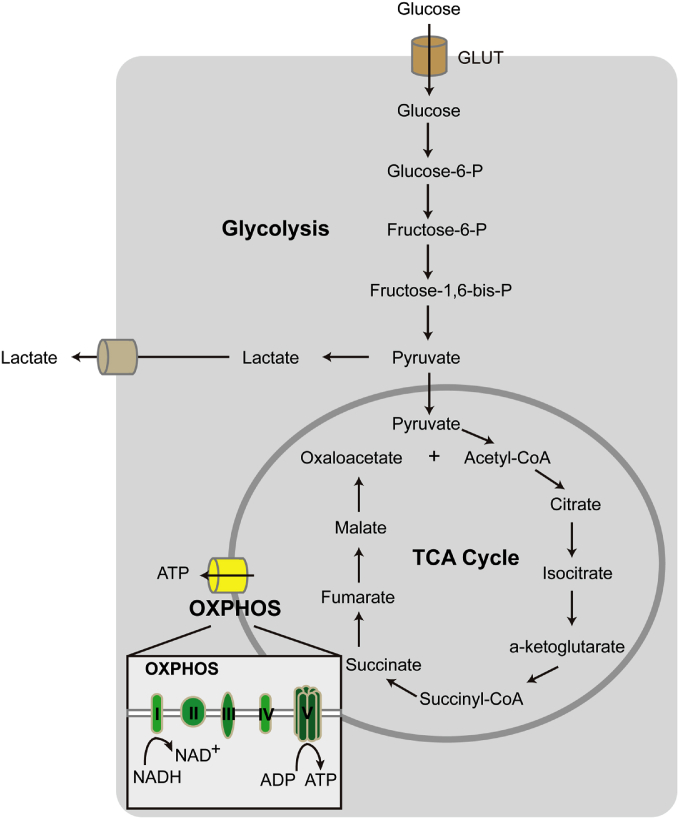
Fig. 2.
Cellular metabolism of glucose. Glucose enters cells through glucose transporter (GLUT) and is converted to pyruvate. In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate and the process is known as glycolysis. In the presence of oxygen, pyruvate enters mitochondria and undergoes TCA cycle. At the mitochondrial membrane, reduced electron carriers, NADH (and FADH2), from the TCA cycle pass their electrons to protein complexes (I to V) for ATP production, a process known as OXPHOS.