Fig. 16.
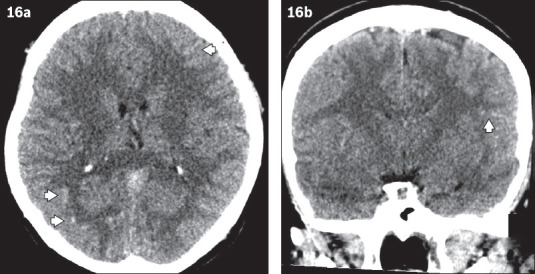
Non-contrast CT images of the brain in (a) axial and (b) coronal views show diffuse sulcal hyperdensity in bilateral cerebral hemispheres (more prominent findings are marked by arrowheads) of a patient who presented with headache. This was initially reported as acute subarachnoid haemorrhage. The patient was subsequently diagnosed with polycythaemia vera. This appearance is due to generalised increased density of the cerebral vessels due to high haematocrit level, and is referred to as pseudosubarachnoid haemorrhage.
