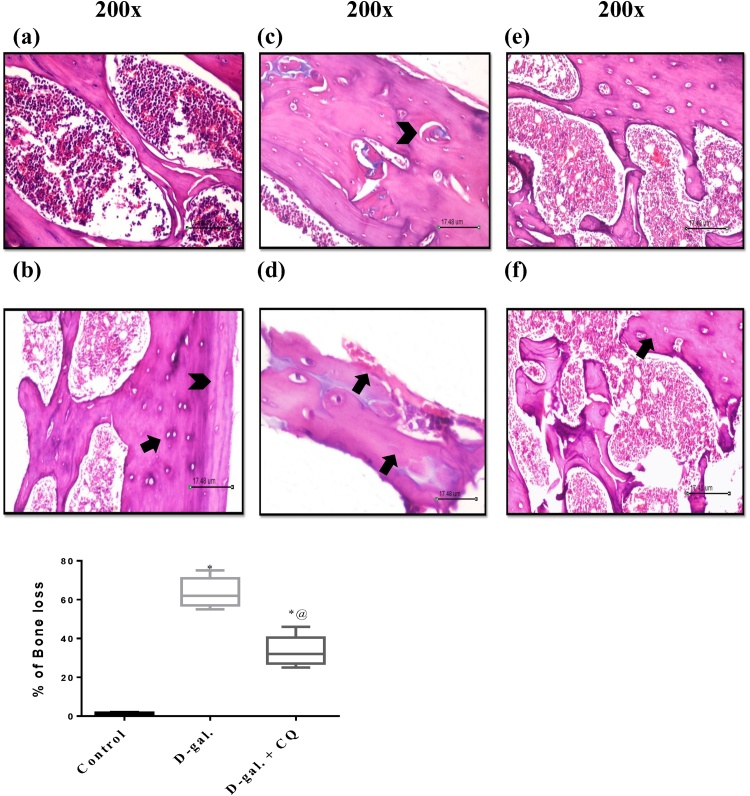
Fig. 9.
Effect of CQ on Histopathological examination in d-gal induced osteoporotic rats. Section of (C) and (D) d-gal induced osteoporosis group shows revealed irregularly sporadically disintegrated endosteal surface and resorption cavities, irregular thickness of the remaining trabeculae, osteoclasts with their acidic compartments and multiple nuclei were detected kept in the eroded bone surface as well as an increment in bone marrow adipocytes compared to the (A) and (B) control groups that showed regular histological structure. Section of (E) and (F) CQ treated group shows mild changes of microarchitectural of bone, trabecular continuity shows some resorption micro-fissures and bony trabeculae enclosing osteocytes in their lacunae. The percentage of osteoporosis were valued by mean of 5 and represented as mean ± S.E.M. Data were statistically estimated using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Variances were deemed statistically significant when *p < 0.05 in contrast to the control group and @ p < 0.05 in contrast to D-gal treated group.