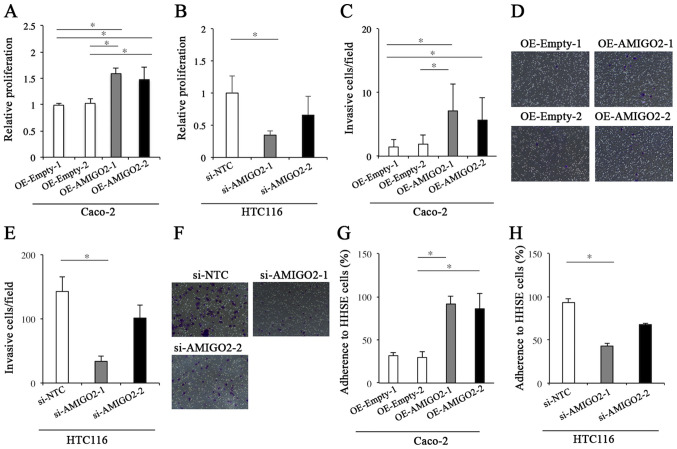
Figure 2.
Proliferation, invasion, and adhesion assays. (A) The proliferation of Caco-2 cells transfected with EX-Mm13004-M02 was significantly higher than that of Caco-2 cells transfected with empty vector. (B) The proliferation of HCT-116 cells transfected with siRNA targeting AMIGO2 was significantly lower than that of HCT-116 transfected with negative control siRNA. (C) The invasive ability of Caco-2 cells transfected with EX-Mm13004-M02 was significantly greater than that of Caco-2 cells transfected with empty vector. (D) The representative images for the invasion assay in each condition of (C) Magnification, ×100. (E) The invasive ability of HCT116 cells transfected with siRNA targeting AMIGO2 was significantly less than that of HCT116 cells transfected with negative control siRNA. (F) The representative images for the invasion assay in each condition of (E) Magnification, ×100. (G) Caco-2 cells transfected with EX-Mm13004-M02 demonstrated significantly increased adhesion to human hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells (HHSECs), when compared with controls. (H) HCT116 cells transfected with AMIGO2 siRNA demonstrated significantly reduced adhesion to HHSECs, when compared with controls. The data were checked for normality with Shapiro Wilk test. Differences in proliferation, invasion, and adhesion were evaluated using the Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn's test. *significant difference between 2 groups by Dunn's test (P<0.05). AMIGO2, adhesion molecule with Ig like domain 2; siRNA, small interfering RNA; OE, overexpression; NTC, non-targeting control; HHSE, human hepatic sinusoidal endothelial.