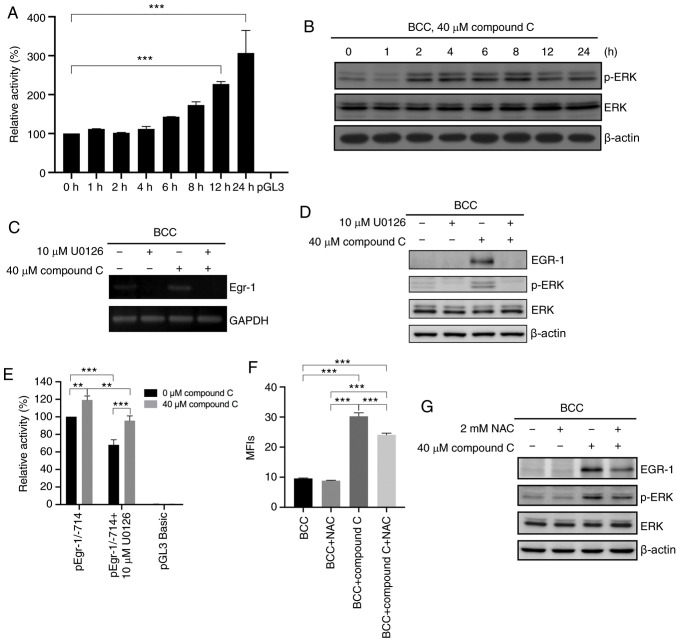
Figure 3.
Compound C upregulates EGR-1 mRNA expression via the ROS-mediated ERK signaling pathway. (A) BCC cells were co-transfected with pGL3-basic-hEGR-1-pro-1/-714 and pGL3 carrying the Renilla luciferase gene for 48 h and then incubated in medium containing 0% FBS and 40 µM compound C for 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12 or 24 h, and analyzed with one-way ANOVA. (B) BCC cells were treated with 40 µM compound C for 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12 or 24 h. Expression levels of p-ERK, ERK and β-actin were detected by immunoblotting. (C and D) BCC cells were pretreated with 10 µM U0126 for 1 h and then treated with 40 µM compound C for 6 h. mRNA and protein expression levels of EGR-1 were detected by reverse transcription PCR and immunoblotting, respectively. (E) BCC cells were co-transfected with pGL3-basic-hEGR-1-pro-1/-714 and pGL4.74 carrying the Renilla luciferase gene for 48 h. Cells were pretreated with 10 µM U0126 for 1 h in serum-free medium and then treated with 0 or 40 µM compound C for 6 h, and analyzed with two-way ANOVA. (F) BCC cells were pretreated with 2 mM NAC for 1 h and then treated with 40 µM compound C for 4 or 6 h to evaluate the ROS or protein expression level. This statistical result was analyzed using one-way ANOVA. (G) Expression levels of EGR-1, p-ERK, ERK and β-actin were detected by immunoblotting with specific antibodies. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. of three independent experiments. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 compared with the control. EGR-1, early growth response-1; BCC, basal cell carcinoma; NAC, N-acetyl-cysteine; p-, phosphorylated.