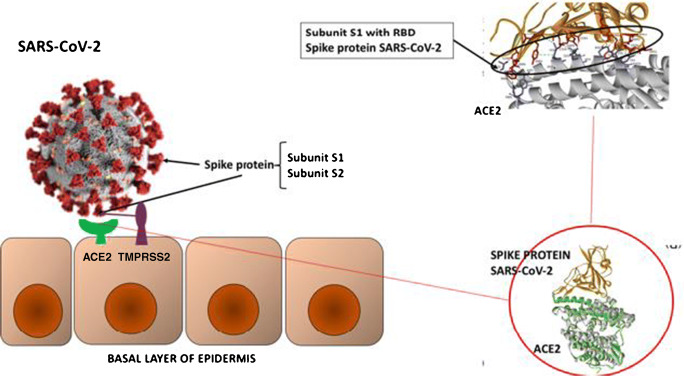
Fig. 2.
On the left-hand side, a schematic representation of the SARS-CoV-2 virus spike protein bound to the host cell (epidermis) via ACE2 and TMPRSS2. The spike protein contains two subunits, S1 and S2, containing the receptor-binding domain (RBD). The RBD is part of the S1 subunit, and the S2 subunit is for membrane fusion. The serine protease TMPRSS2 cleaves the spike glycoprotein between S1 and S2, which helps the virus to integrate into the cell membrane and allow it to enter the host cell. At the molecular level, the binding includes amino acids, hydrogens bonds, and electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions. On the right-hand side, crystallographic image of ACE2 and the spike protein and RBD within the S1 subunit binding to the receptor site of ACE2