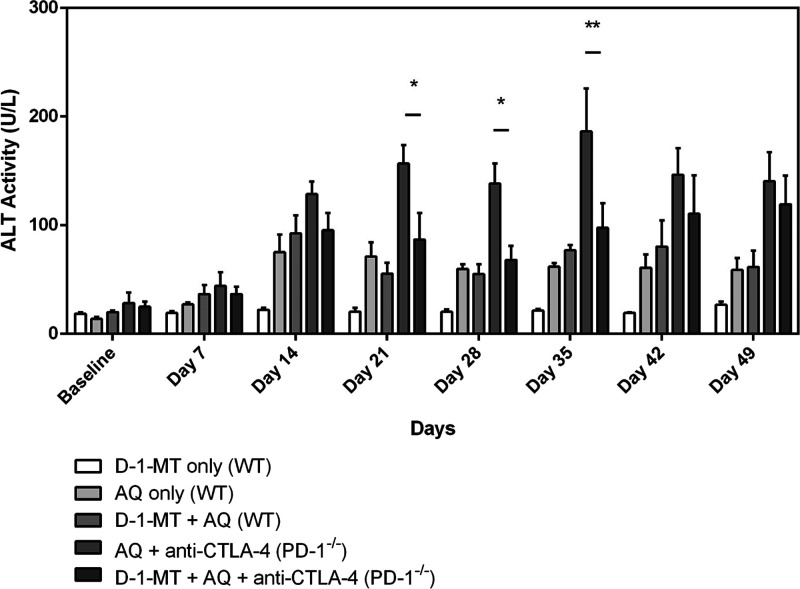
Figure 3.
D-1-MT decreases the liver injury caused by AQ in the impaired immune tolerance model but not the milder injury in wild-type mice. D-1-MT represents treatment with D-1-MT (4 mg/mL in drinking water), AQ represents treatment with AQ (0.2% w/w in the diet), and WT is short for wild-type animals. All PD-1–/– animals received weekly intraperitoneal injections of anti-CTLA-4 (300 μg/dose) along with the starting injections on days −3 and −1 prior to drug treatment with AQ and/or D-1-MT. ALT activity levels from day 21 to day 35 were significantly higher in the PD-1–/– mice treated with AQ and anti-CTLA-4 in comparison to those in which D-1-MT was added. The data represent the mean ± SEM, and statistical significance was tested using a two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; *p < 0.05 or **p < 0.01 between AQ + anti-CTLA-4 (PD-1–/–) and D-1-MT + AQ + anti-CTLA-4 (PD-1–/–) animals (n = 3 mice/group).