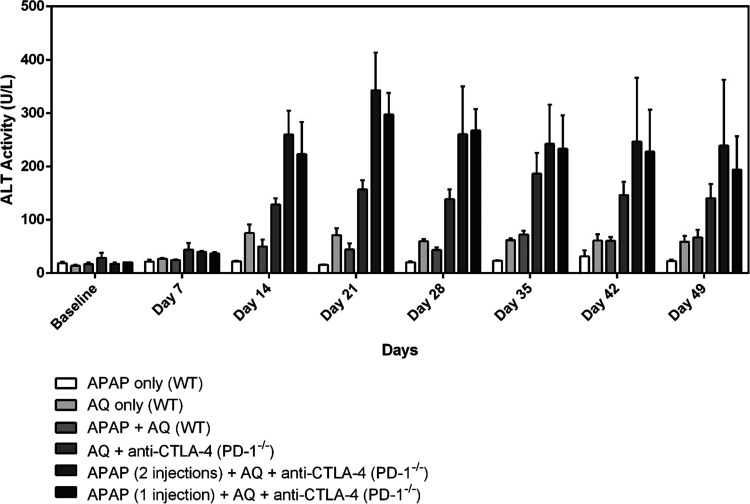
Figure 6.
Treatment with intraperitoneal injections of APAP (300 mg/kg/dose) appeared to further increase serum ALT levels in PD-1–/– female C57BL/6 mice treated with amodiaquine (0.2% w/w) in the diet, but the difference was not statistically significant. “APAP only” is acetaminophen (given as two doses at 0 and 48 h) and “APAP + AQ” is acetaminophen (given as two doses at 0 and 48 h) with AQ in the diet; WT is short for wild-type mice. In the APAP-treated PD-1–/– animals, APAP was administered intraperitoneally as a single dose (at 0 h) or two doses (at 0 and 48 h) for comparison. In the PD-1–/– groups, all animals received AQ in the diet and weekly intraperitoneal injections of anti-CTLA-4 (300 μg/dose) along with the starting injections on days −3 and −1 prior to drug treatment with APAP and AQ. The data represent the mean ± SEM. No significant differences were detected in any of the groups using a two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; n = 3 mice/group.