Fig. 8.
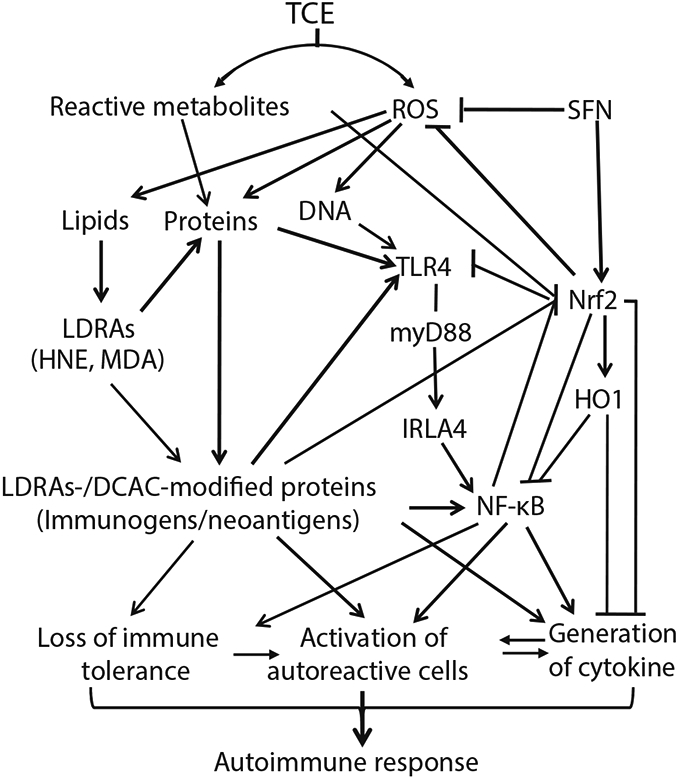
Schematic presentation of our hypothesis. TCE exposure causes oxidative stress and oxidative modification of proteins which interact with TLR signaling and Nrf2-NF-κB pathways, and lead to elevated lymphocyte proliferation, cytokine generation and loss of immune tolerance, eventually resulting to autoimmunity in MRL+/+ mice. Improvement in oxidative stress, dysregulation of TLR signaling and impairment of Nrf2-NF-κB pathway following SFN supplementation attenuates increased activation of lymphocytes and release of cytokines, ultimately leading to alleviation of inflammation/autoimmunity mediated by TCE exposure.
