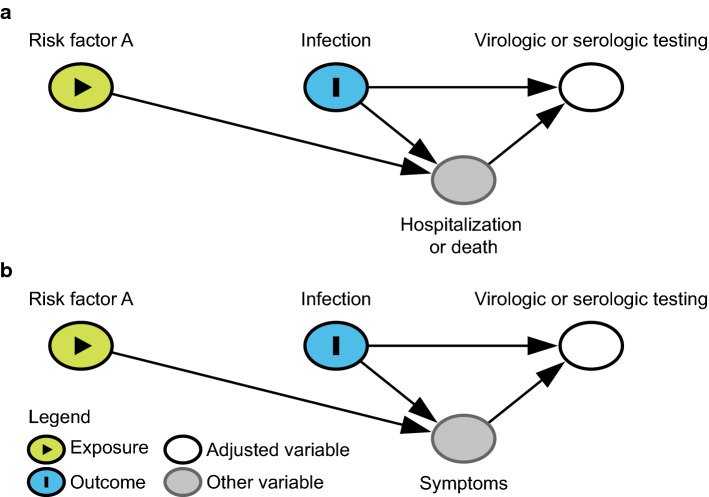
Fig. 5.
Directed acyclic graph under the null hypothesis showing the possible structure of selection bias due to a exclusion from testing and b differential likelihood of testing. Under the null hypothesis (of no effect of Risk Factor A on COVID-19 infection) selection bias can be in either direction depending on whether Risk Factor A increases or decreases the likelihood of (a) severe disease or (b) symptoms among infected individuals. The figures are simplified to illustrate these particular biases so make the strong assumption of no additional unmeasured confounding (i.e., no common causes of any two variables in the figure)