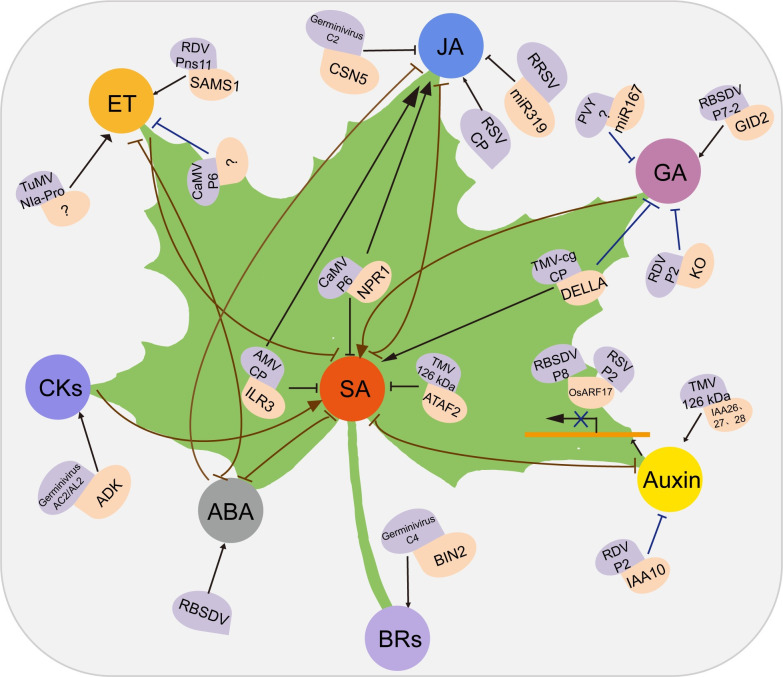
Fig 2. Plant hormone–virus interactions.
Different virus proteins and host factors interact and lead to positive (arrows) or negative (blocked lines) effects on plant hormone biosynthesis or signaling pathways. The roles of SA, JA, and ET in plant defense responses have been intensively studied. Auxin and GAs are mainly related to the host phenotype after virus infection. CKs and BRs are involved in plant–virus interactions. Different plant hormones display synergetic or antagonistic crosstalk during plant–virus interactions, and microRNAs are used by viruses to target plant hormone pathways. For details, see text. ABA, abscisic acid; AMV, alfalfa mosaic virus; BIN2, BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE 2; BR, brassinosteroid; CaMV, cauliflower mosaic virus; CK, cytokinin; ET, ethylene; GA, gibberellic acid; GID2, GIBBERELLIN-INSENSITIVE DWARF2; JA, jasmonic acid; PVY, potato virus Y; RBSDV, rice black streaked dwarf virus; RDV, rice dwarf virus; RRSV, rice ragged stunt virus; RSV, rice stripe virus; SA, salicylic acid; SAMS1, S-adenosyl-l-methionine synthase 1; TMV, tobacco mosaic virus; TuMV, turnip mosaic virus.