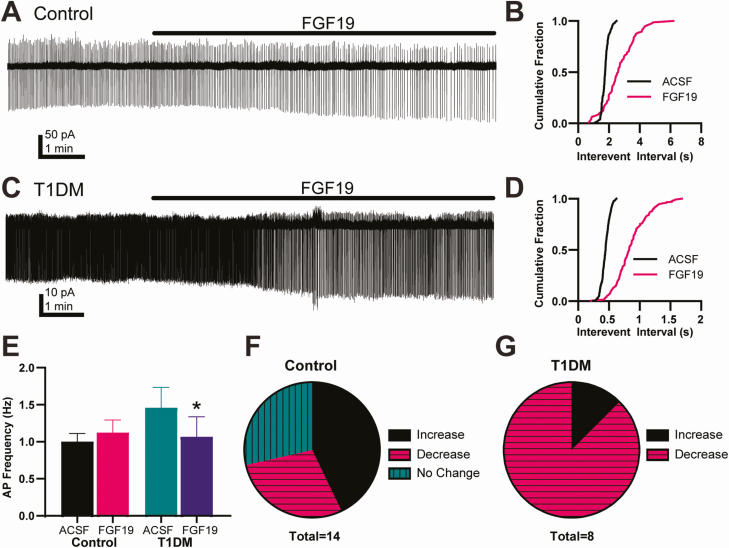
Figure 4.
FGF19 variably affects action potential frequency. (A) Representative traces showing effects of FGF19 on spontaneous sodium-dependent action potential currents (IAP) in cell-attached recordings in a DMV neuron from a control mouse. (B) Cumulative probability plot of the traces in (A). (C) Representative traces showing effects of FGF19 on IAP frequency in a DMV neuron from a T1DM mouse. (D) Cumulative probability plot of the traces in (C). (E) FGF19 did not alter mean IAP frequency in control mice (n = 14; P > 0.05) but significantly decreased IAP frequency in T1DM mice (n = 8; P < 0.05). Asterisk indicates significance vs ACSF. (F) Relative proportion of neurons with responses to FGF19 application in neurons from control mice indicate variable responses. (G) Proportions of responses in T1DM mice suggests a that FGF19 decreases IAP frequency in most neurons. Recorded from control, 2 male and 2 female, and T1DM, 3 male and 2 female mice.