Table 4. Recycling PUs through Depolymerization and Polycondensationa.
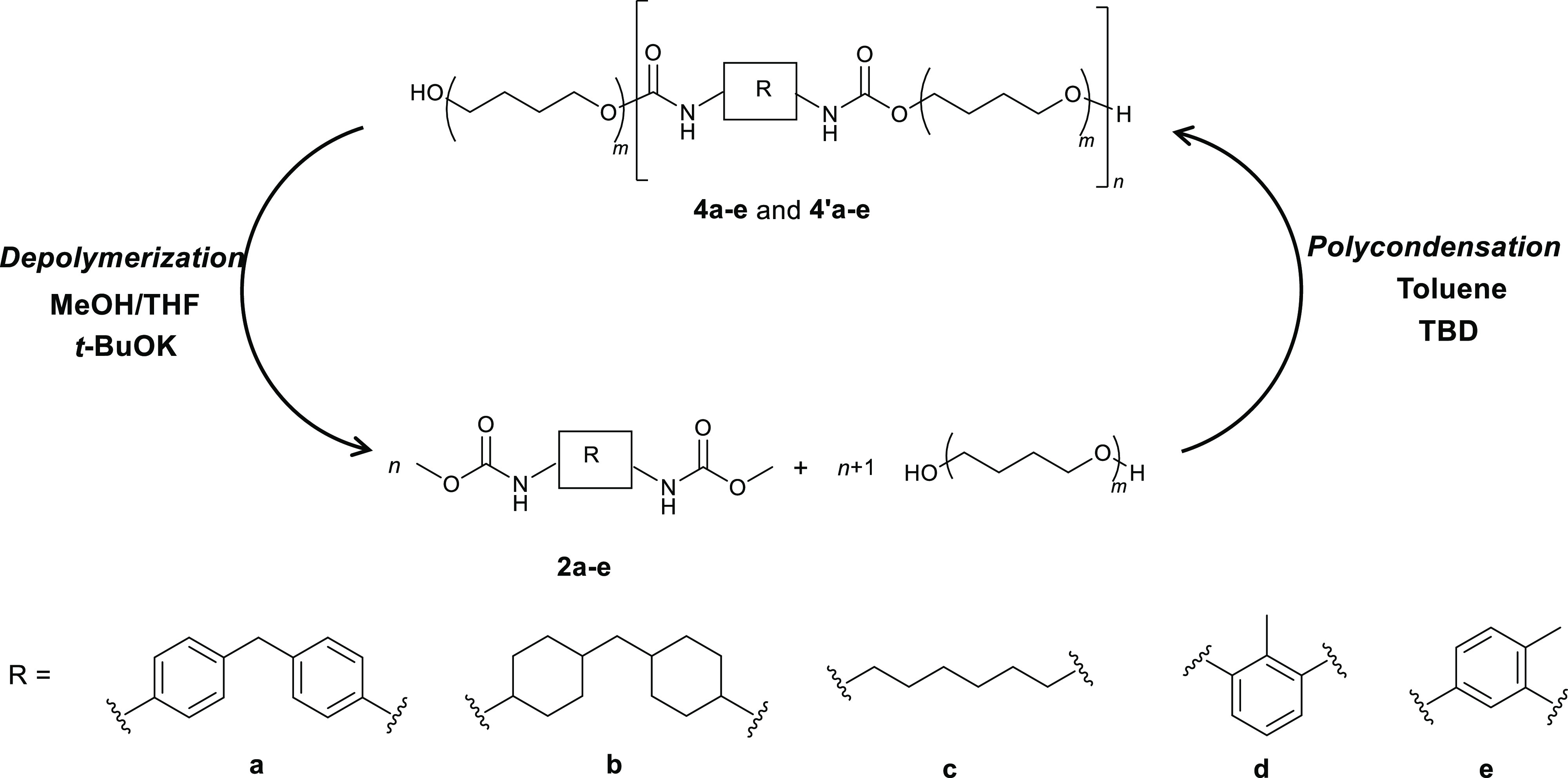
| depolymerization
of PU into monomers |
repolymerized
PU |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | 4 | R | Mw/Mnb,f | Mwb | yield (%)c | 4′ | Mwd,f | Mw/Mnd,f | yield (%)e |
| 1 | 4a | 2a | 1.21 | 28,000 | 85 | 4′a | 18,100 | 1.34 | 51 |
| 2 | 4b | 2b | 1.24 | 28,000 | 73 | 4′b | 10,800 | 1.30 | 31 |
| 3 | 4c | 2c | 1.24 | 22,000 | 89 | 4′c | 13,000 | 1.35 | 65 |
| 4 | 4d | 2d | 1.38 | 14,000 | 91 | 4′d | 8900 | 1.42 | 56 |
| 5 | 4e | 2e | 1.33 | 20,000 | 81 | 4′e | 10,000 | 1.33 | 41 |
Depolymerization conditions as described in Table 2. Polymerization: the same process as described in Table 3 (with extra 0.1 equiv of monomer 2).
PU synthesized by diisocyanate approach.
Isolated yield (monomer 2, by column chromatography) of depolymerization, calculated for the urethane group.
PU synthesized by transcarbamoylation.
Yield of polymerization.
Determined by SEC.
