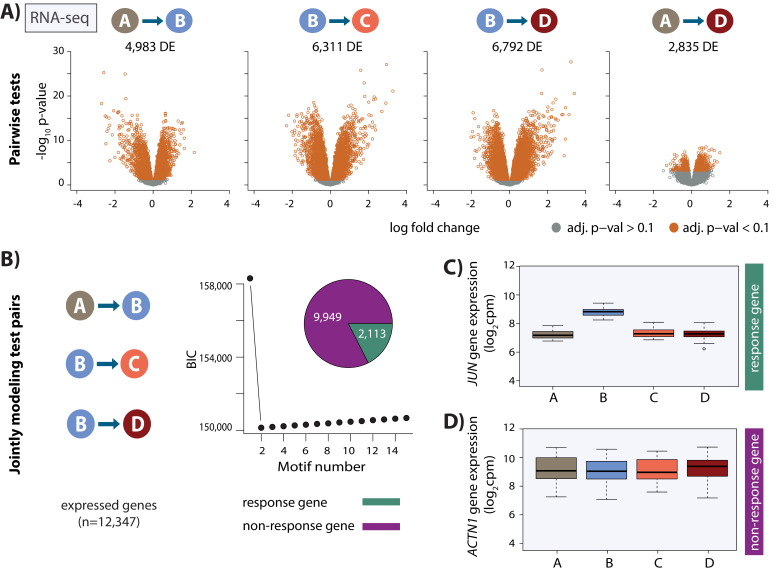
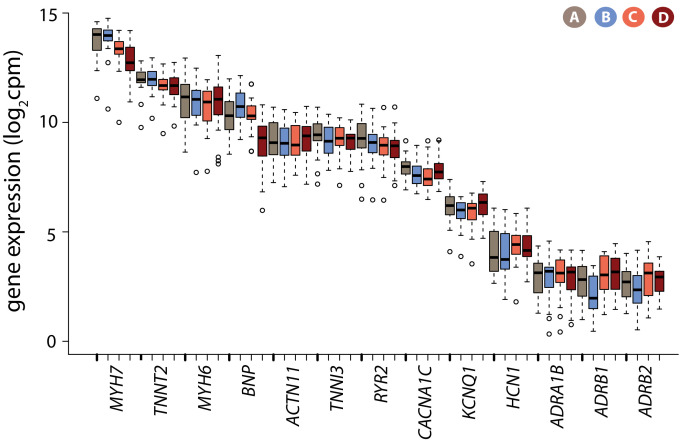
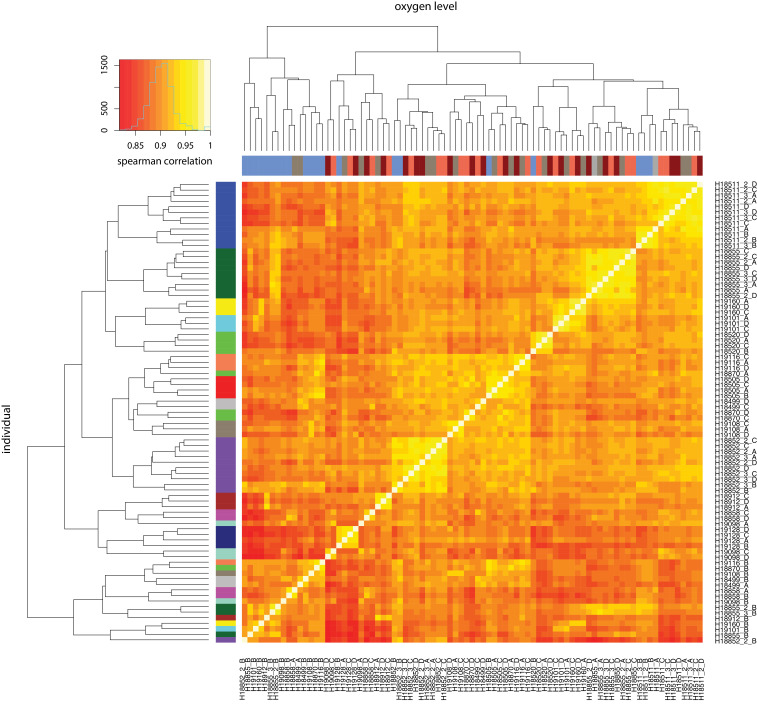
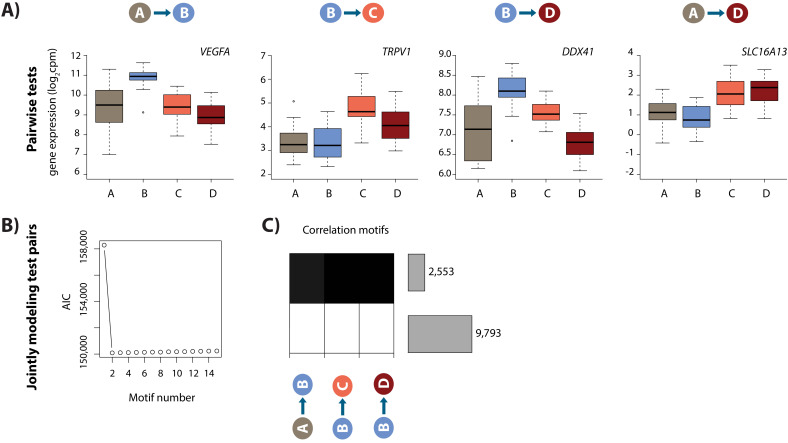
Figure 2. Thousands of gene expression changes occur following hypoxia and re-oxygenation.
(A) Volcano plots representing genes that are differentially expressed (DE) between pairs of conditions (orange dots). (B) Bayesian information criterion (BIC) at increasing numbers of Cormotif correlation motifs following joint modeling of pairs of tests. Genes with a posterior probability of being differentially expressed p>0.5 across all tests are defined as ‘response genes’ and those with p<0.5 as ‘non-response genes’. Inset shows the proportion of all expressed genes that are classified as response genes (green), and non-response genes (magenta). (C) Expression levels of JUN, a response gene, during the course of the experiment. (D) Expression levels of ACTN1, a non-response gene.