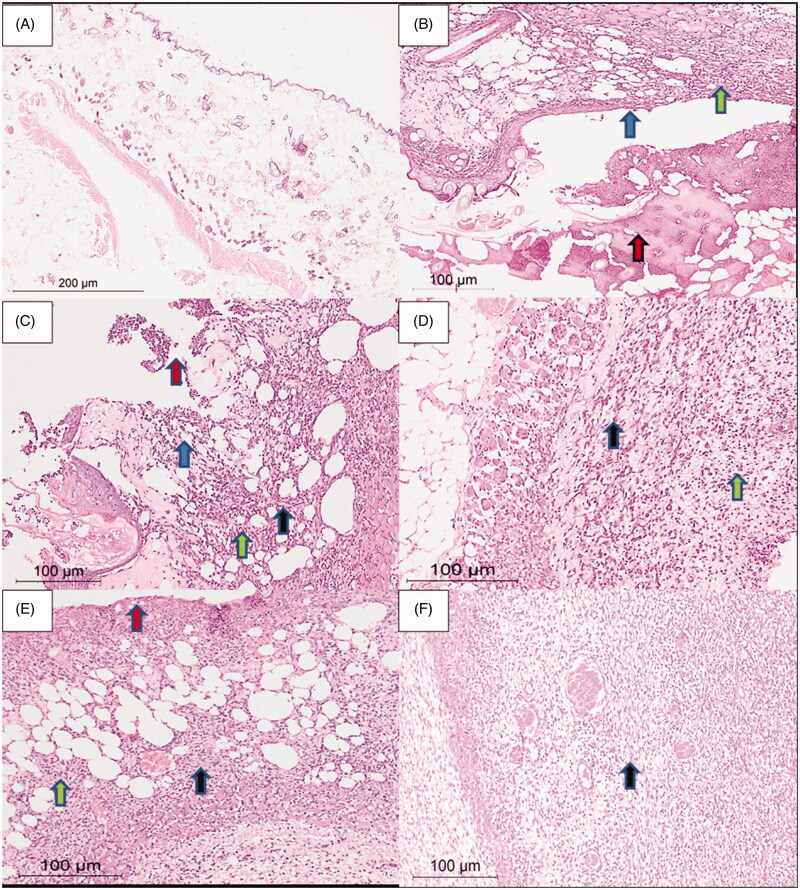
Figure 9.
Rat skin samples after the six-day treatment. (A) The normal skin control group showed intact skin surface epithelium and normal dermal and subcutaneous tissues without inflammation (H&E, ×100). (B) Group 1 – no treatment: wide ulceration of the surface (blue arrow) covered by an excessive amount of fibrinoid material (red arrow). The dermis and the subcutaneous tissue show mixed acute and chronic inflammatory cells (green arrow), H&E ×200. (C) Group 2 – cinnamon oil gel: smaller skin ulcers (blue arrow) covered by fibrinoid material (red arrow). The dermis and subcutaneous tissue show inflammatory infiltrate (green arrow) and fibrosis (black arrow) H&E ×200. (D) Group 3 – NLC-cinnamon oil colloid: wide areas of granulation tissue (green arrow) admixed with fibrosis denoting the healing process (black arrow) H&E ×200. (E) Group 4 – NLC blank gel: focal ulcerated area covered by fibrinoid material (red arrow) with small areas of granulation tissue and fibrosis (black arrow) extending to the dermis and subcutaneous tissue with moderate mixed acute and chronic inflammatory infiltrate (green arrow), H&E ×200. (F) Group 5 – NLC-cinnamon oil gel: wide areas of granulation tissue and fibrosis occupying the whole dermis (black arrow), H&E ×200.