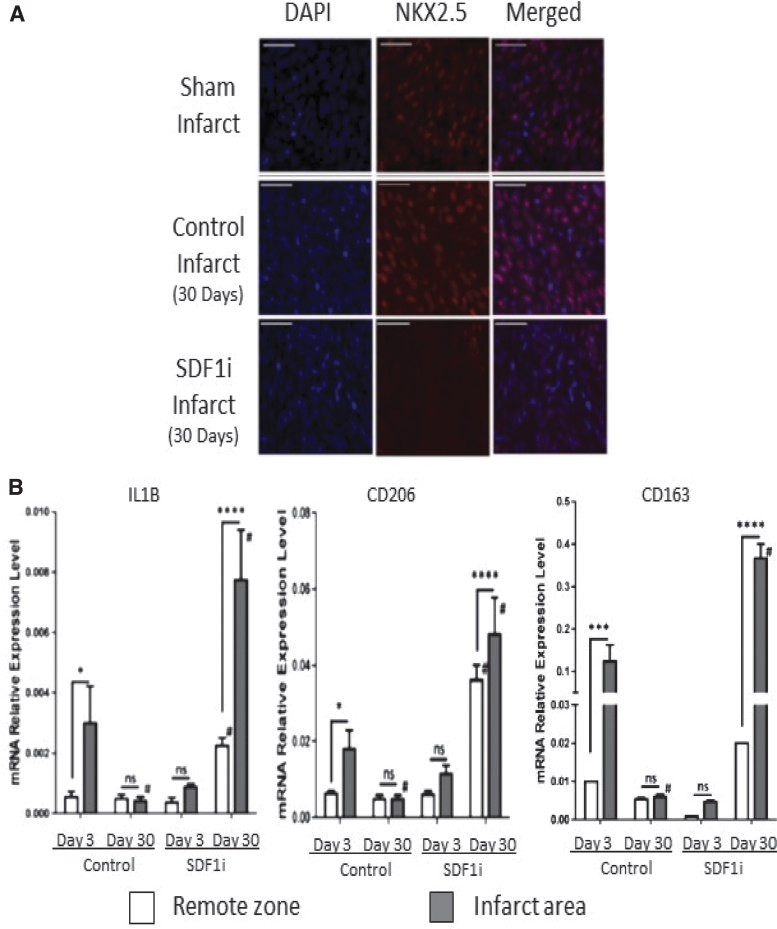
Figure 8.
Inhibition of SDF1α minimizes regenerative phenotype (A) SDF-1α inhibition blocks fetal cardiac cell repopulation after myocardial infarction (MI). Representative images show (scale bars = 50 μm) staining with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue), immunohistochemistry for nkx2.5 (red), and merged DAPI and nkx2.5 of the apex of fetal sham operation and fetal infarct treated with mutant SDF-1α transgene (SDFi) at 30 days.(B) Real-time PCR analysis of the gene expression of macrophage phenotype markers in the fetal hearts 3 and 30 days after myocardial infarction, with SDF-1α inhibition (day 3, n = 5; day 30, n = 4) or without SDF-1α inhibition (day 3, n = 5; day 30, n = 5). Interleukin-1β (IL-1b), CD206, and CD163 gene expression were calculated after normalizing to 18S. Two-way analysis of variance followed by Fisher's least significant difference post hoc test was used to analyze the data. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001 comparing RZ (unshaded bars) to IA (shaded bars) in each group. #p < 0.0001 comparing RZ on day 3 to RZ on day 30 or IA on day 3 to IA on day 30. (D = day; mRNA = messenger ribonucleic acid; ns = not significant). SDF-1α, stromal-derived factor-1α.