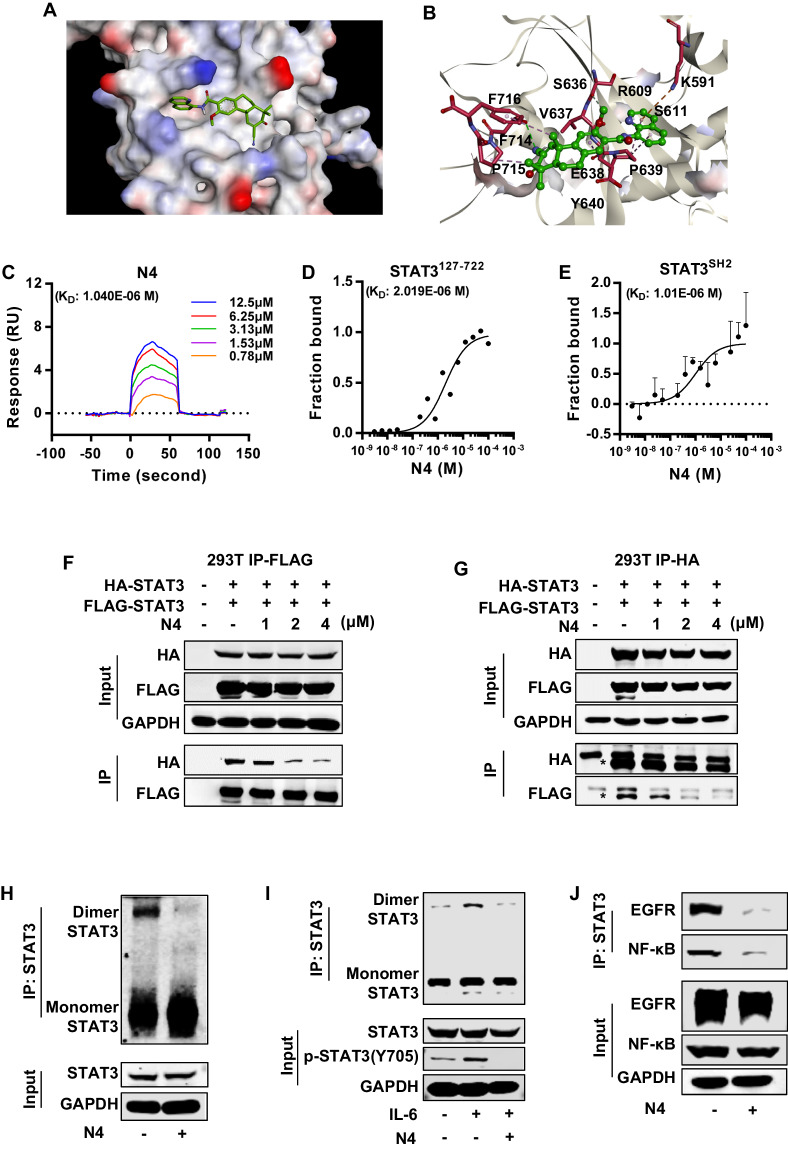
Fig. 3. N4 interacts with the STAT3-SH2 domain and interferes with the STAT3-EGFR and STAT3-NF-κB interactions.
A, B Molecular docking model revealed that N4 binds to the SH2 domain of STAT3. C–E The binding between N4 and STAT3 was examined in (C) SPR and (D) MST experiments. His-STAT3127-722 protein was purified and used to examine the affinity between STAT3 and N4. (E) The binding between N4 and STAT3SH2 was confirmed in MST assays. STAT3-SH2 protein was purified and labeled. N4 was serially diluted and mixed with equal volumes of labeled STAT3SH2 protein. The MST signal was measured, and the data were analyzed by MO analysis software. F, G The FLAG-tag and HA-tag STAT3 expression plasmid was transfected into 293 T cells, followed by the addition of the indicated concentrations of N4. After 24 h, cells were lysed, and immunoprecipitation experiments were performed as described in Materials and Methods. H N4 represses STAT3 dimerization in pancreatic cancer cells. I After a 24 h treatment with 2 μM N4, pancreatic cancer cells were stimulated with IL-6 for 30 min. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with STAT3 overnight. The precipitates were washed, suspended in non-reducing sample buffer, and boiled for 10 min. The indicated antibodies were used for western blot assays. J N4 inhibits STAT3-EGFR and STAT3-NF-κB interaction in pancreatic cancer cells. PANC-1 cells were treated with 2 μM N4 for 24 h. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with STAT3 and blotted with the indicated antibodies.