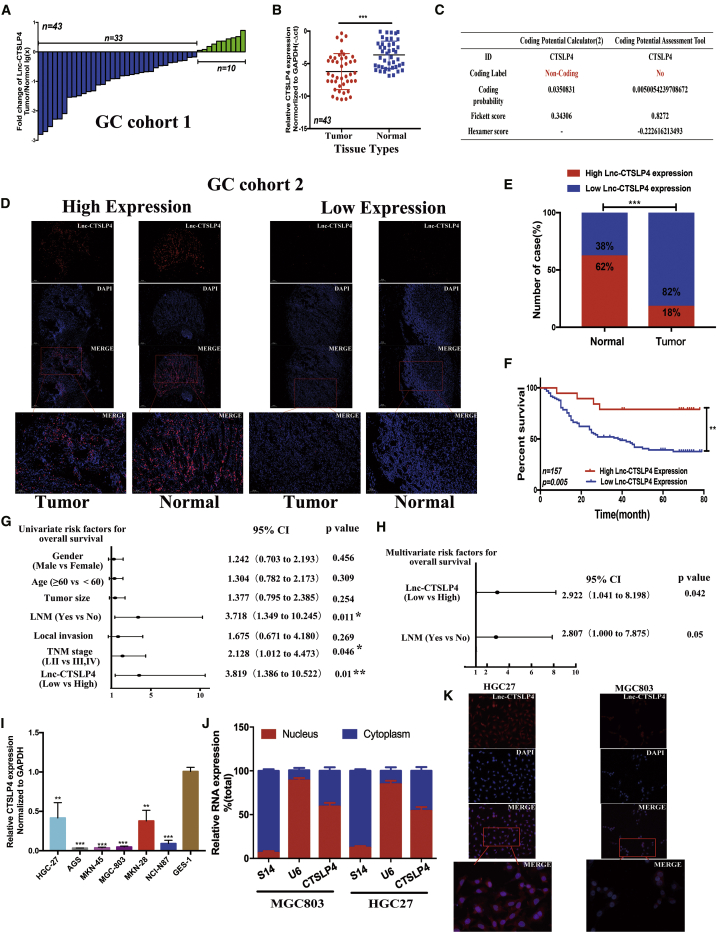
Figure 1.
Lnc-CTSLP4 expression is downregulated in tumor tissues and inversely associated with prognosis of GC patients
(A) The expression of lnc-CTSLP4 in 43 GC tissues (GC cohort 1, the ratio of GC tumor tissues versus adjacent non-tumor tissues [−ΔCt]). (B) Expression levels of lnc-CTSLP4 in GC tumor tissues (GC cohort 1) and adjacent normal tissues (−ΔCt, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001). (C) The coding ability of lnc-CTSLP4 calculated by CPC2 and CPAT. (D) RNA-FISH analysis of lnc-CTSLP4 expression in the paraffin-embedded GC tumor tissues and adjacent non-tumor tissues (red: lnc-CTSLP4; blue: nuclear; n = 157, scale bars: 100 μm and 200 μm). (E) lnc-CTSLP4 high and low expression rate in GC (GC cohort 2, RNA-FISH). (F) Kaplan-Meier analysis of the overall survival of GC (GC cohort 2, n = 157). The log-rank test revealed statistical significance between the low CTSLP4 expression group (n = 129) and the high CTSLP4 expression group (n = 28). (G and H) Univariate (G) and multivariate (H) analysis for prognostic features of GC patients (n = 157). (I) Expression of lnc-CTSLP4 in GC cell lines and a normal gastric epithelium cell line, GES-1. (J) The expression of lnc-CTSLP4 in the subcellular fractions of GC cells (MGC803 and HGC27, qRT-PCR; U6 and S14 were used as nuclear and cytoplasmic markers, respectively). (K) Representative RNA-FISH imaging of lnc-CTSLP4 (red) in GC cells (red: lnc-CTSLP4; blue: DAPI; magnification: 200× and 400×).