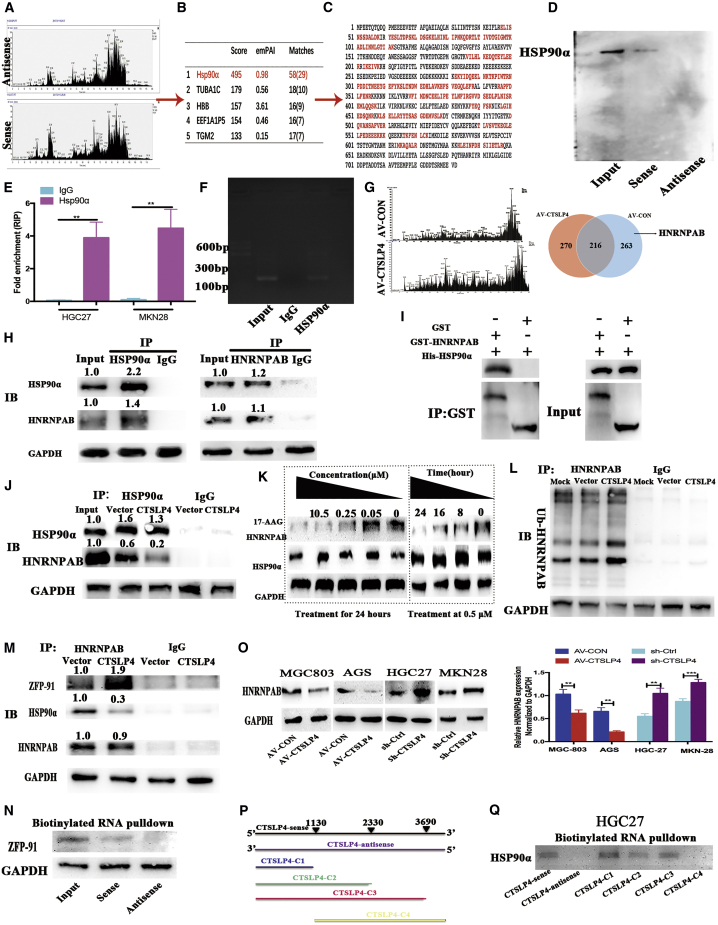
Figure 3.
Lnc-CTSLP4 binds to Hsp90α and promotes the degradation of HNRNPAB protein by recruiting ZFP91
(A and B) RNA-pulldown assays and LC-MS/MS analysis of proteins that are specifically bound to lnc-CTSLP4 (anti-sense RNA as a negative control, A represents proteins that bound to sense or antisense of lnc-CTSLP4 and B represents top 5 proteins identified). (C) The peptide sequences of Hsp90α binding with lnc-CTSLP4 (red: matched peptide sequences). (D) Hsp90α was detected by Western blot after RNA-pulldown assays (A). (E and F) RIP and qRT-PCR analysis for the specific binding of Hsp90α to lnc-CTSLP4. ∗∗p < 0.01. (G) Co-IP followed by LC-MS/MS analysis showed that the Hsp90α could bind to HNRNPAB in the absence of lnc-CTSLP4. (H) The interaction of Hsp90α and HNRNPAB was verified by Co-IP in MGC803 cells. (I) GST-pulldown analysis of the binding of Hsp90α and HNRNPAB. (J) Analysis of proteins obtained in Co-IP in lnc-MGC803-AV-CTSLP4 and MGC803-AV-CON cells. (K) The protein levels of HNRNPAB and Hsp90α in MGC803 cells treated with 17-AAG (an Hsp90 inhibitor) for the indicated doses and times. (L) Ubiquitin modification of HNRNPAB in MGC803-AV-CTSLP4 and MGC803-AV-CON cells. (M) Co-IP and Western blot analysis of the binding of HNRNPAB to ZFP91 or Hsp90α in MGC803-AV-CTSLP4 and MGC803-AV-CON cells. (N) The specific binding of ZFP91 to lnc-CTSLP4 verified by RNA-pulldown assays (negative control: anti-sense). (O) Western blot analysis of HNRNPAB protein in GC cells (MGC803, AGS, HGC27, MKN28) after overexpression (AV-CTSLP4) or shRNA knockdown of lnc-CTSLP4 (sh-CTSLP4). (P) Truncated versions of lnc-CTSLP4, C1 (1-1130 bp), C2 (1-2330 bp), C3 (1-3690 bp), and C4 (1130-3690 bp) according to the predicted lnc-CTSLP4 structure. (Q) Western blot detection of Hsp90α after RNA-pulldown with biotinylated RNAs for different constructs of lnc-CTSLP4 or its antisense strand (negative control).