Figure 6.
Elevated LV Filling Pressures Promote Left Atrial Dysfunction, Leading to Combined Pre- and Post-Capillary Pulmonary Hypertension
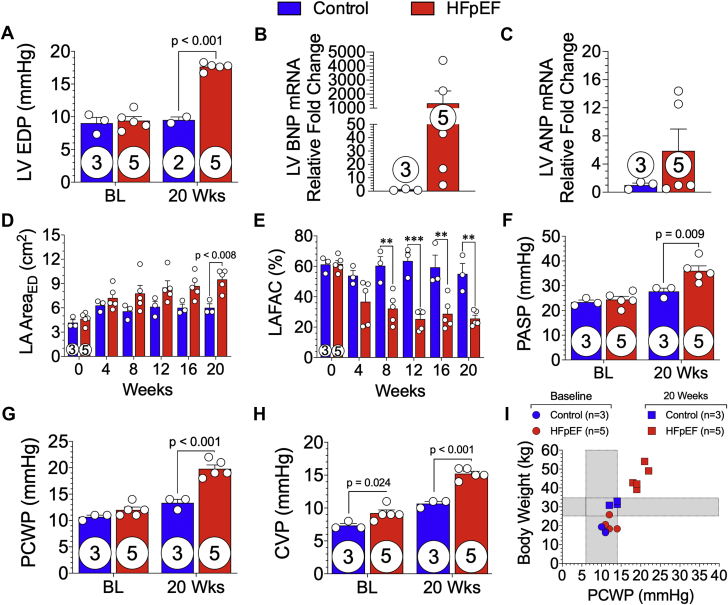
Invasive LV hemodynamic measurements were acquired at baseline (BL) and 20 weeks from control and HFpEF minipigs. (A) LV end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) was calculated. (B) B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and (C) atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) mRNA expression of LV tissue. (D) Left atrial (LA) area at end-diastole (ED) and (E) LA fractional area change (LAFAC) were measured from subcostal 2-dimensional B-mode echocardiographic images acquired at baseline and every 4 weeks during the 20-week study from control and HFpEF minipigs. (F) Pulmonary artery systolic (PASP) and (G) pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) and (H) central venous pressure (CVP) were measured at baseline and 20 weeks in control and HFpEF minipigs. (I) The relationship of body weight to PCWP at baseline and 20 weeks was plotted. Values are mean ± SEM; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001, for significantly different versus control. Numbers in circles represent the number of animals analyzed. Abbreviations as in Figures 1 and 3.