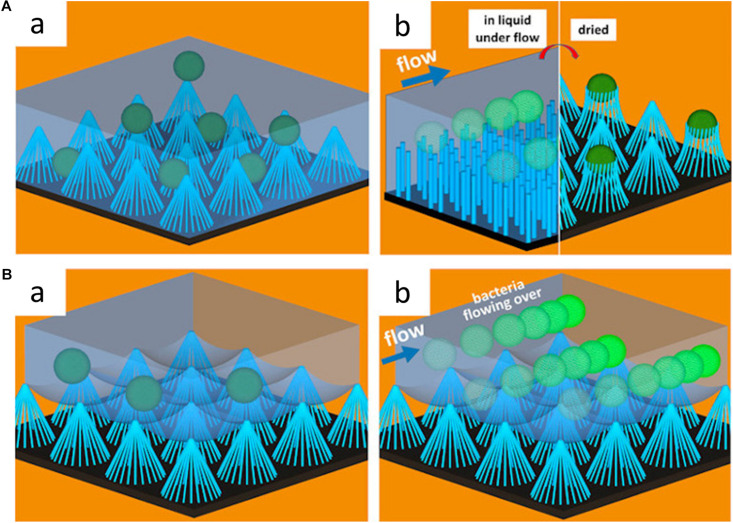
FIGURE 5.
Schematic illustration of the effects of surface wettability on bacterial adhesion under dynamic conditions. (A) Schematic illustration of S. aureus adhesion on hydrophilic nanopillar surfaces under static and fluid conditions. In the static condition, bacteria adhere to both the nanopillar tips and troughs, while bacteria adhere to only the nanopillar tips under fluid conditions. Adapted from Hizal et al. (2017). (B) Schematic illustration of S. aureus adhesion on hydrophobic nanopillar surfaces under static and fluid conditions. In the static condition, the bacteria float over the entrapped air layer, and bacteria are swept away by fluid flow. Reprinted with permission from Hizal et al. (2017) Nanoengineered Superhydrophobic Surfaces of Aluminum with Extremely Low Bacterial Adhesivity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9, 12,118–12,129. Copyright© 2017, American Chemical Society.