Figure 7.
Cardiomyocyte miR-146a regulates cardiac I/R injury in a cyclophilin D-dependent manner
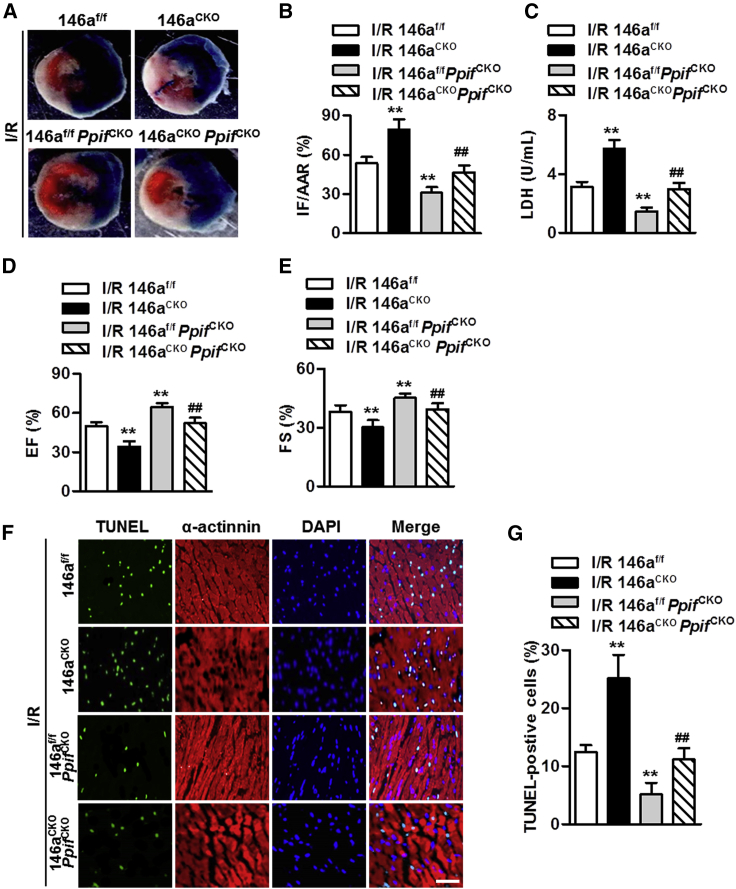
(A and B) miR-146af/f/MHC-Cre mice (miR-146aCKO) were crossed with Ppiff/f/MHC-Cre mice (PpifCKO) to obtain miR-146aCKOPpifCKO mice and underwent I/R surgery. Myocardial infarct was visualized by Trypan blue (A) and 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining and assessed as the ratio of infarcted area (IF) to area at risk (AAR) (IF/AAR) (B). ∗∗p < 0.01 versus I/R 146af/f; ##p < 0.01 versus I/R 146aCKO, n = 6 per group. (C) Measurements of LDH serum levels. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus I/R 146af/f; ##p < 0.01 versus I/R 146aCKO, n = 10 per group. (D and E) Analysis of echocardiographic left ventricular ejection fraction (EF, D) and percentage fractional shortening (FS, E) data at the end of 24 h reperfusion. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus I/R 146af/f; ##p < 0.01 versus I/R 146aCKO, n = 8 per group. (F) Representative images of myocardial tissue sections stained with TUNEL and anti-α-actinin antibody. (G) QuantiGication of apoptotic cardiomyocytes in each group. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus I/R 146af/f; ##p < 0.01 versus I/R 146aCKO, n = 6 per group.