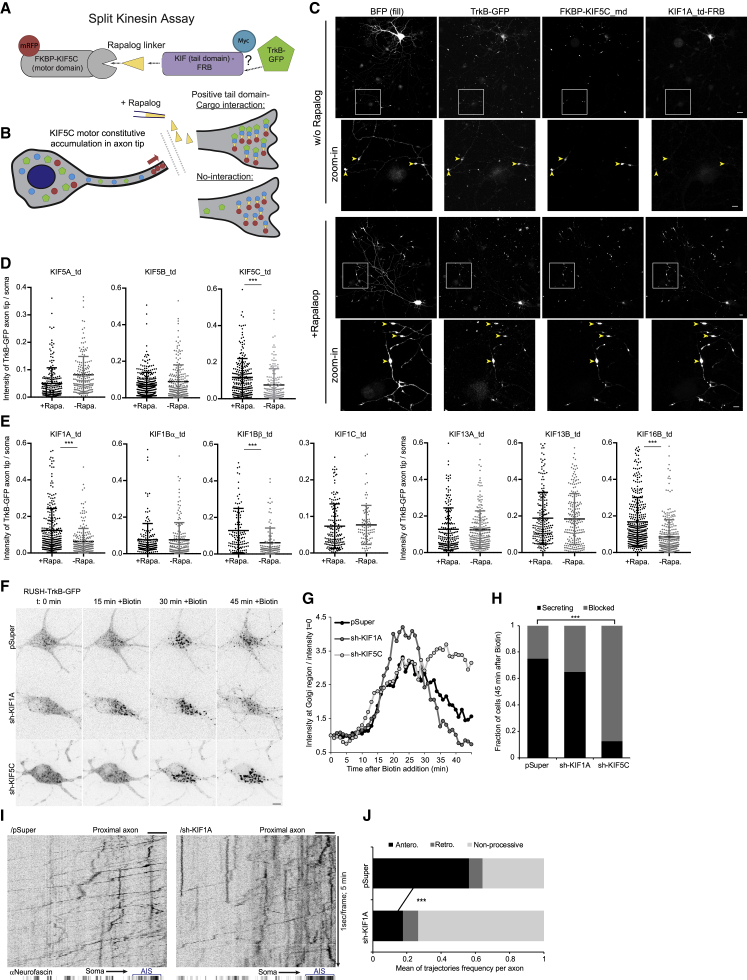
Figure 6.
The kinesins KIF5C and KIF1A regulate the axonal trafficking of TrkB
(A and B) Schemes of the split-kinesin assay (SKA) used in the experiments presented in (C–E).
(A) The components of the SKA with TrkB-GFP as cargo reporter.
(B) Rapalog addition induces the mobilization of the kinesin tail domain and accumulation at the axon tips due to tight interaction with the constitutively motile motor KIF5C. Interaction between the kinesin tail domain and the TrkB cargo will result in accumulation of TrkB in the axon tips together with the KIF-td and KIF5C-md where rapalog is added.
(C–E) Neurons were transfected with SKA components described in (A) and treated either with control (−Rapa) or rapalog treatment (+Rapa) for 16–24 h before fixation, followed by immunostaining for myc-tagged KIF-td.
(C) Images of the soma and axon tips (highlighted in zoom-in insets) of neurons assayed for TrkB-KIF1A interaction with and without rapalog addition. Scale bars, 10 and 5 μm (insets).
(D) SKA results for TrkB-GFP and Kinesin-1 family. (E) SKA results for TrkB-GFP and Kinesin-3 family. Data in (D–E) are TrkB-GFP signal in individual axon tips, normalized to the signal in the soma of each axon tip. Lines depict mean and SD. ∗∗∗Two-sided Student’s t test, p < 0.001. Data points were collected from the following number of axon tip: KIF5A: 221 and 181; KIF5B: 303 and 214; KIF5C: 239 and 176; KIF1A: 270 and 219; KIF1Bα: 167 and 162; KIF1Bβ: 118 and 110; KIF1C: 158 and 86; KIF13A: 187 and 230; KIF13B: 204 and 208; and KIF16B: 357 and 288 for +Rapa and −Rapa conditions, respectively.
(F–H) Neurons co-transfected with RUSH-TrkB-GFP and shRNA constructs against KIF1A or KIF5C were treated with biotin and RUSH-TrkB-GFP at the soma was live imaged for 45 min at 1 frame/min.
(F) Time series images of representative neurons expressing RUSH-TrkB-GFP with specified shRNA constructs.
(G) Time plots of RUSH-TrkB intensity at the Golgi (normalized to t = 0) of neurons shown in (F).
(H) Frequency of neuron categorized as secreting or blocked in response to 45 min of biotin. ∗∗∗Chi-square test p < 0.001, n = 28, 20, and 16 neurons from 5, 3, and 3 experiments for pSuper, sh-KIF1A, and sh-KIF5C conditions, respectively.
(I and J) Neurons expressing RUSH-TrkB-GFP and pSuper or shKIF1A were stained for neurofascin (AIS). Time-lapse imaging was carried in a time window of 45–90 min after addition of biotin. Images series were captured at 1 frame/s for 5 min each.
(I) Kymographs of proximal axon segments of representative neurons.
(J) Frequency of trajectory directionality in the proximal segment of the axon. Trajectories with net displacement of less than 15 μm in the course of 5 min were counted as non-processive. The processive traces were classified based on their directionality as either retrograde or anterograde. Bars depict mean ratio of trajectories per each time series (axon). ∗∗∗Two-sided Student’s t test (anterograde fraction) p < 0.001, n = 12 and 10, based on 234 and 180 trajectories of pSuper and sh-KIF1A conditions, respectively, from 3 independent experiments. Scale bars, 5 μm.