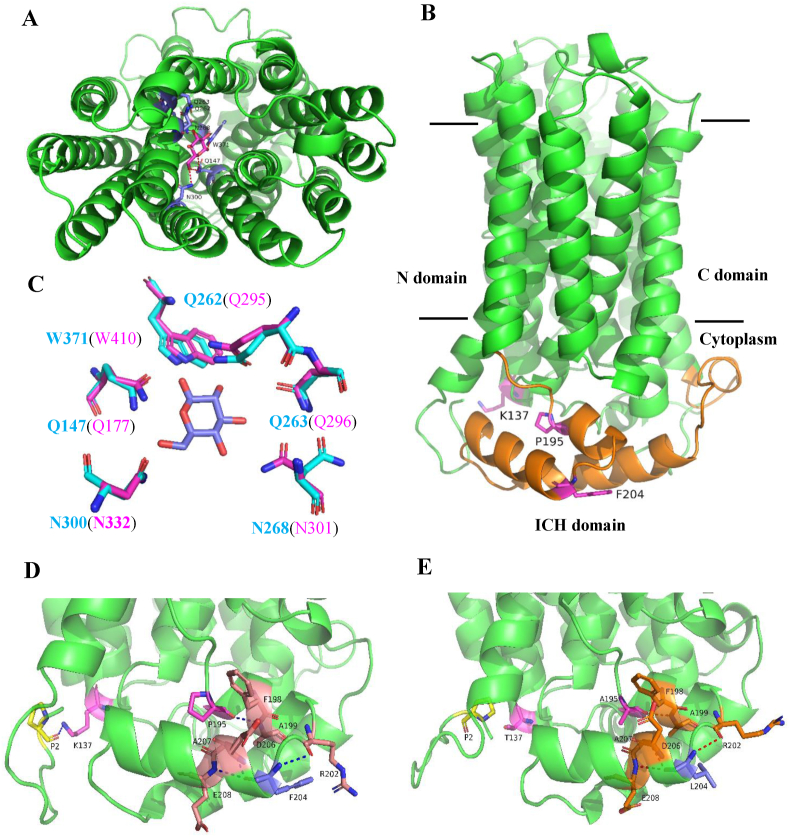
Fig. 9.
A 3D model of E. coli GalP generated based on the crystal structure of Arabidopsis thaliana symporter STP10 (PDB: 6H7D). (A) The structure (viewed from the periplasmic face) represents an outward-facing conformation in complex with D-glucose. (B) Side view of the modeled GalP structure in a ribbon representation. The intracellular helical bundle (ICH) domain is shown in orange, where the mutated residues in GalP are presented in pink sticks. (C) Comparison of the glucose binding sites of E. coli GalP (blue) and STP10 (pink). (D) For the wild-type residue K137, its backbone ε-ammonium group (NH3+) is attached to the carboxyl group of P2, while (E) the mutated residue K137T is out of H-bond distance of the P2 residue. In comparison to the wild type, the other two mutated residues P195A and F204L are still bound to the adjacent residues to form the flexible ICH domain. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)