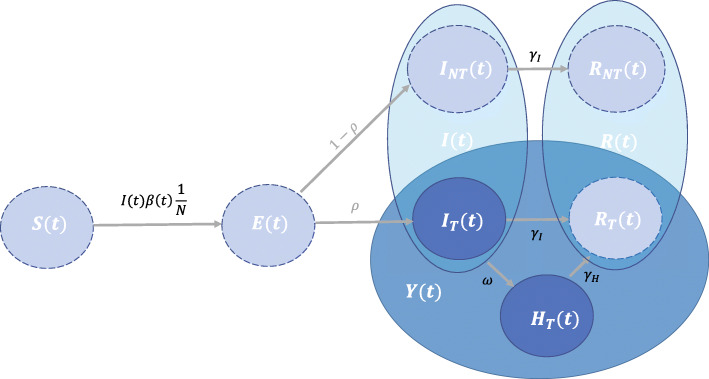
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the SEIR model. When there are both susceptible individuals, S(t), as well as infectious individuals, I(t), a susceptible individual gets exposed E(t) at an exponential rate of β(t)S(t)/N. Once exposed it takes a Weibull distributed time before the individual becomes infectious. The individual is tested with probability ρ, I(t), and might subsequently be hospitalized, H(t)). Infectious individuals that will not be tested, INT(t), cannot be hospitalized. The infectious period of non-hospitalized infectious individuals is assumed to follow an Exponential distribution after which the individuals are transferred to the removed states