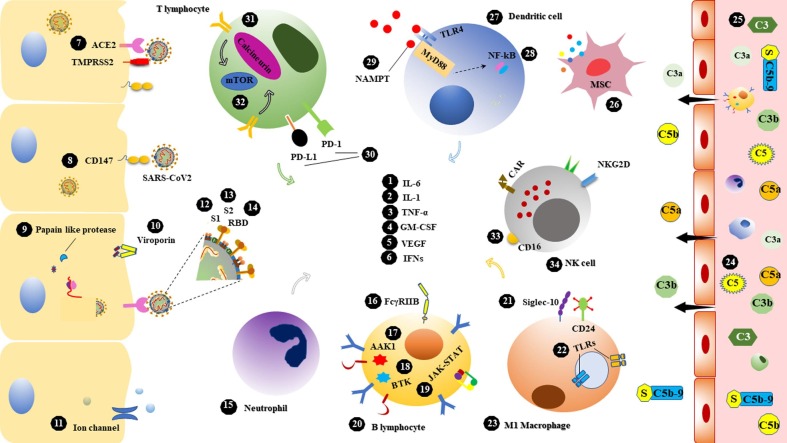
Fig. 2.
Potential targets in the immunotherapy of SARS-CoV2 infection. 34 molecular and cellular targets associated with host immune responses as well as factors involved in SARS-CoV2 pathogenesis have been conceived. 1) interleukin (IL)-6, prominent driver of hyperinflammatory syndromes which participates in lung pathology 2) IL-1, one of the main pillars of cytokine storm 3) tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), a proinflammatory cytokine that involves in alveolar and epithelial injury 4) granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), involved in both the pathogenesis of COVID-19-like syndromes and the physiology of the lungs 5) vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), increases vascular permeability and is associated with hypoxia, edema, and lung damage 6) interferons (IFNs), induce antiviral defense in various cells 7) angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), main receptor for SARS-CoV2 entrance via S protein 8) CD147, mediates SARS-CoV2 invasion to host cells 9) Papain like protease, essential coronavirus protease to produce replicase complex 10) Viroporin, inducing inflammasome and related to viral life cycle 11) Ion channel, targets of dewetting monoclonal antibodies to block water flow and viral spread 12) S1, The major subunit of the spike protein and mediates ACE2 binding 13) S2, up to 88% sequence homology with SARS-CoV and contains conserved motifs for cross-neutralizing antibodies 14) receptor binding domain (RBD), the main part of the S1 subunit and the target of many neutralizing antibodies 15) neutrophil, the causative agent of excessive inflammation related to poor prognosis 16) FcγRIIB, an immunosuppressant receptor constrains antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) by some antibodies 17) AP2-associated protein kinase 1 (AAK1), contributor of receptor-mediated viral endocytosis 18) Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK), activate in macrophage polarization, humoral immunity and hyperinflammatory outcomes 19) Janus kinase (JAK)-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT), the major arbitrators in proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines signaling 20) B lymphocyte, reservoir of antibody production and involvement in inflammatory responses 21) Sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin 10 (Siglec-10), mediates B cell tolerance and dendritic cell suppression following CD24 interaction 22) endosomal and membrane-bound toll like receptors (TLRs) ligands, inducing antiviral responses, 23) M1 macrophage, cause of inflammation and tissue damage 24) C5 & 25) C3, role in hyper inflammatory syndromes and thrombotic microangiopathy 26) mesenchymal stem cell (MSC), anti-inflammatory and tissue repairing potentials 27) Dendritic cell, the main APC at the onset of inflammatory responses 28) nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) driver of lethal inflammation 29) Nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase (NAMPT), released following physical stress and mediated hyper inflammation 30) programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) & programmed cell death (PD-1), immune checkpoint inhibitors cause T cell exhaustion 31) Calcineurin, role in cytokine storm and early T cell activation 32) mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), related to the complications of obesity and inflammation 33) CD16, role in antibody mediated cytotoxicity and viral clearance 34) natural killer (NK) cell, immune homeostasis and eradicating viral infections.