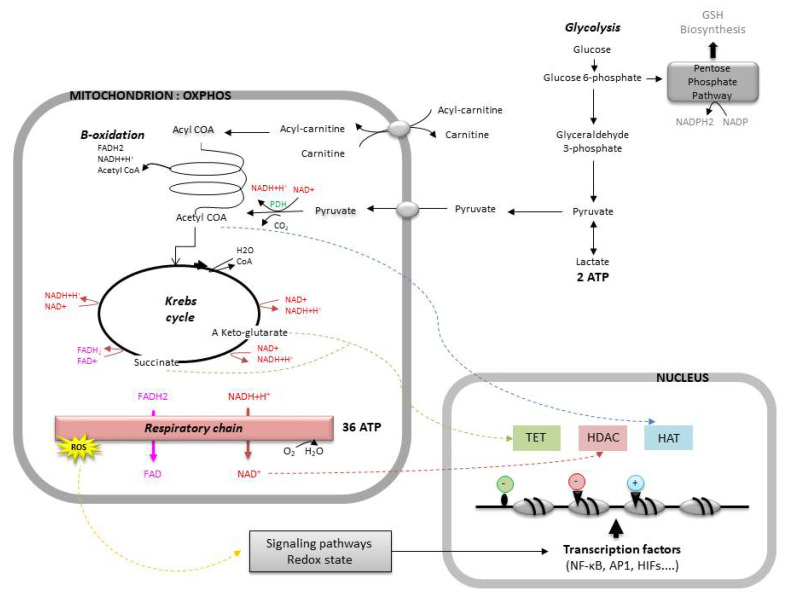
Figure 3.
The role of mitochondria in cell metabolism, signaling pathways, and genic expression. The cell produces its energy (ATP) via oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) or via anaerobic glycolysis. The embryo uses pyruvate or glucose as the main source of energy according to its stage of development. The mitochondrial function produces intermediate metabolites and reactive oxygen species (ROS) that are involved in signaling pathways, redox homeostasis, and genic expression. Enzymes implicated in epigenetic regulation: Ten eleven translocase (TET), histone deacetylase (HDAC), and histone acetyltransferase (HAT). Transcription factors: κB family (NF-κB), activator protein-1 family (AP1), and hypoxia-inducible transcription factors (HIFs). GSH, glutathione; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase.