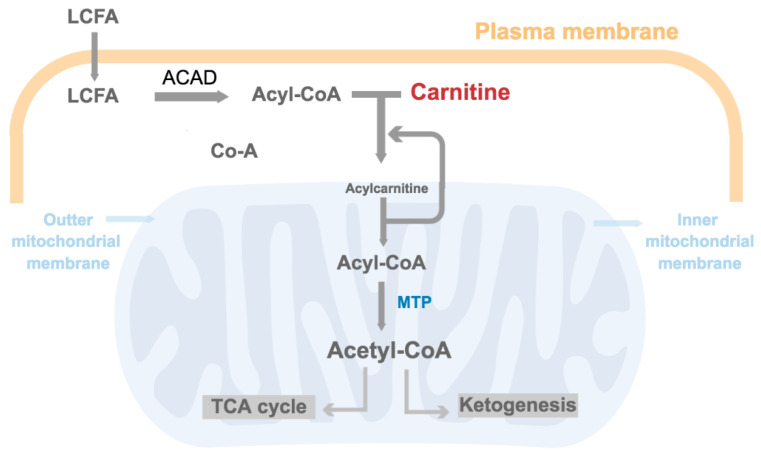
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of mitochondrial fatty acid entry and beta oxidation. Long chain fatty acid (LCFA) is activated by bonding with CoA upon cell entry. Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (ACAD) catalyzes this first reaction. This molecule, now an acyl-CoA, is shuttled through the mitochondrial membrane by forming an ester bond with carnitine, thus generating acylcarnitine. Once inside the mitochondria, acylcarnitine is broken down to produce free carnitine, which can be recycled to shuttle in further fatty acids in the mitochondria. The long chain acyl-CoA generated is then oxidised to produce acetyl-CoA, a process catalysed by mitochondrial trifunctional protein (MTP). Acetyl-CoA can be utilised in the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) cycle or participate in ketogenesis.