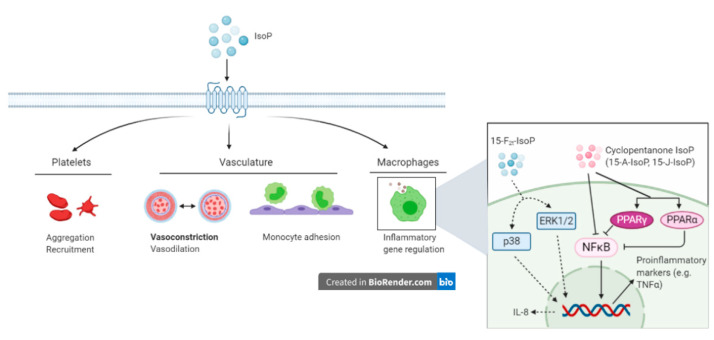
Figure 4.
Putative actions of isoprostanes (IsoP) through the thromboxane receptor. Isoprostanes partake in vascular regulation and inflammation through their actions on platelets, the vasculature, and macrophages. During inflammation, IsoP affect monocyte adhesion to the endothelium and alter macrophage inflammatory genes. Insert box: 15-F2t-isoprostane modifies monocyte adhesion and increases interleukin-8 production via p38 and ERK1/2. Anti-inflammatory effects of IsoP are mediated by signaling through nuclear factor kappa B and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor. IsoP = isoprostane; ERK = extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; NFκB = nuclear factor kappa B; PPAR = peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; IL = interleukin. Created with BioRender.com.