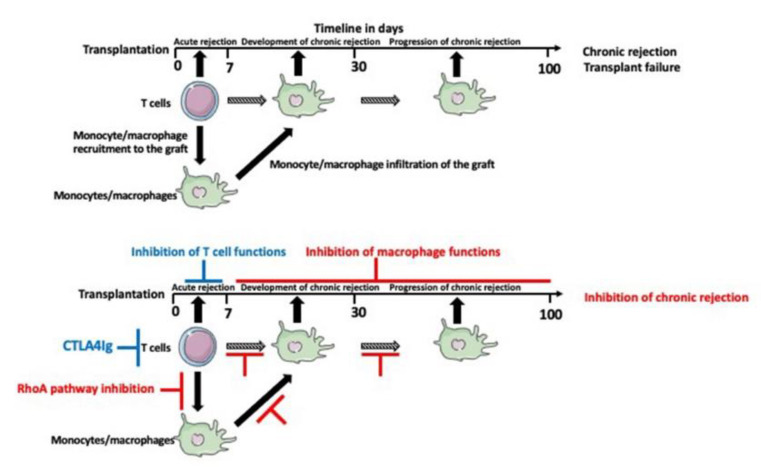
Figure 5.
Timeline of transplant rejection and therapeutic intervention in the mouse cardiac transplantation model. The acute rejection, which occurs a few days after transplantation depends mainly on the T cells. The immunosuppressive drugs targeting T cells such as CTLA4Ig (in the mouse model) inhibit acute rejection but not the chronic rejection, which relies mainly on the macrophages. Administration of the RhoA pathway inhibitors within the first week of post-transplantation inhibits macrophage recruitment into the graft and inhibits chronic rejection.