Fig. 5.
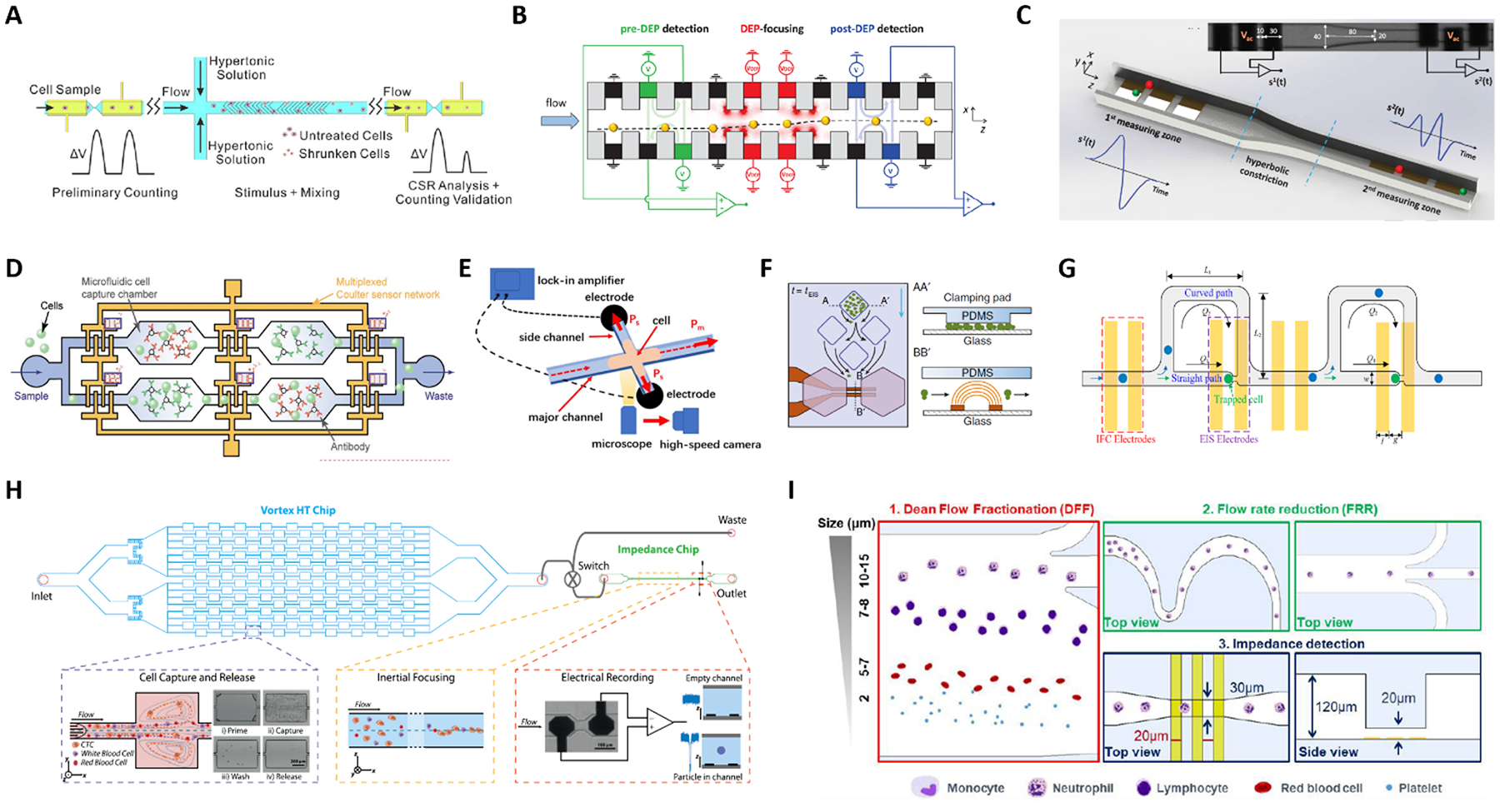
(A-D) Platforms with two or more electrical sensing zones, which are separated by: (A) a region of hypertonic stimulation, (B) a region of dielectrophoretic focusing, (C) a hyperbolic constriction, and (D) antigen specific capture chambers. (E-I) Hybrid platforms combining impedance cytometry with: (E) high-speed optical imaging, (F) time-lapse microscopy of growing cells, (G) impedance spectroscopy of individual trapped cells, (H) a Vortex chip for selective enrichement, and (I) two inertial focusing stages for Dean flow fractionation and flow rate reduction, respectively. See Section 2.5 and Table 1C–D for details. Images were adapted with permission from (A) ref. 119, copyright 2019 Elsevier B.V, (B) ref. 120, copyright 2019 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, (C) ref. 44, copyright 2020 IEEE, (D) ref. 125, 2019 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, (E) ref. 127, copyright Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2020, (F) ref. 128, copyright The Author(s) 2018, (G) ref. 129, copyright 2019 American Chemical Society, (H) ref. 52, copyright 2019 International Society for Advancement of Cytometry, (I) ref. 63, copyright The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019.
