Figure 1:
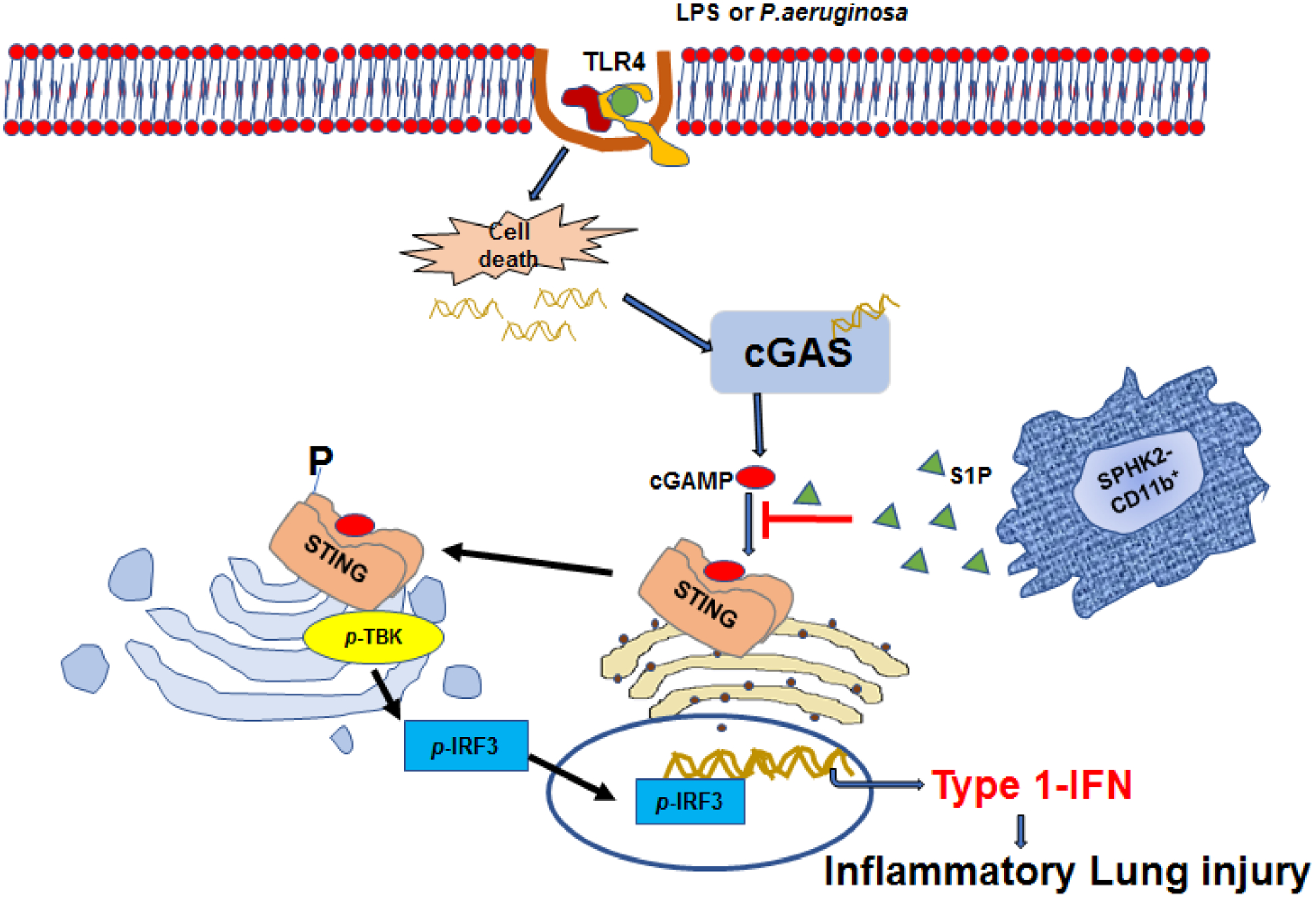
Upon recognition of LPS or Gram -ve bacteria like Pseudomonas aeruginosa by TLR4, there is cell death, which leads to the generation of dsDNA. This ds DNA is sensed by the DNA-sensing receptor cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) which acts as substrate to catalyze the formation of cGAMP, which is a second messenger to activate STING. Activated STING dimerizes and translocate from the ER to the perinuclear region via Golgi to recruit and promote phosphorylation of TBK1-IRF3, which subsequently drives translocation of p-IRF3 to the nucleus to produce type 1-IFN. The SPHK2-CD11b+ recruited macrophages release SIP which compete with cGAMP and inhibit binding of cGAMP to STING, thus blocks the translocation of STING and phosphorylation of TBK1 and IRF3 and generation of type 1-IFN.
