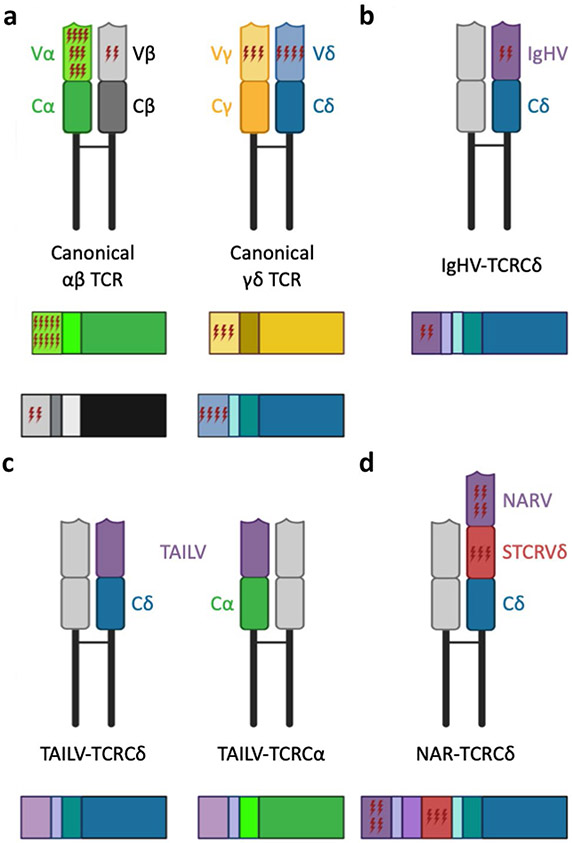
Fig. 2.
Cartoon depictions of putative assembled T cell receptors (TCR, top of each panel) and transcripts (bottom of each panel) illustrating the relative extent of somatic hypermutation (SHM) acquired by variable (V) regions of TCR chains in nurse sharks. a While V regions of all canonical TCR chains assimilate SHM, alpha chain incorporates significantly more mutation than other chains [αβTCR: alpha chain, α (green); beta chain, β (black); and γδ5TCR: gamma chain, γ (gold); delta chain, δ (blue)]; b Immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) V gene segments associated with TCRδ (or rarely TCRα) accumulate mutation within CDR2 regions at rates substantially lower than when used by immunoglobulin C regions; c TCR-associated Ig-like V (TAILV) gene segments, which associate with either TCRδ or TCRα C, do not appear to undergo SHM; d doubly-rearranging NAR-TCRδ are composed of two variable domains that undergo separate RAG-mediated VDJ recombination events—a membrane-distal IgNAR-like V domain (NARV, purple) supported by a membrane-proximal TCR δV domain (STCRδV, red) and associate with TCR δC incorporate few mutations to wither V domain [NAR: nurse shark (or new) antigen receptor; RAG: recombination activating genes]. Figure created with BioRender.com