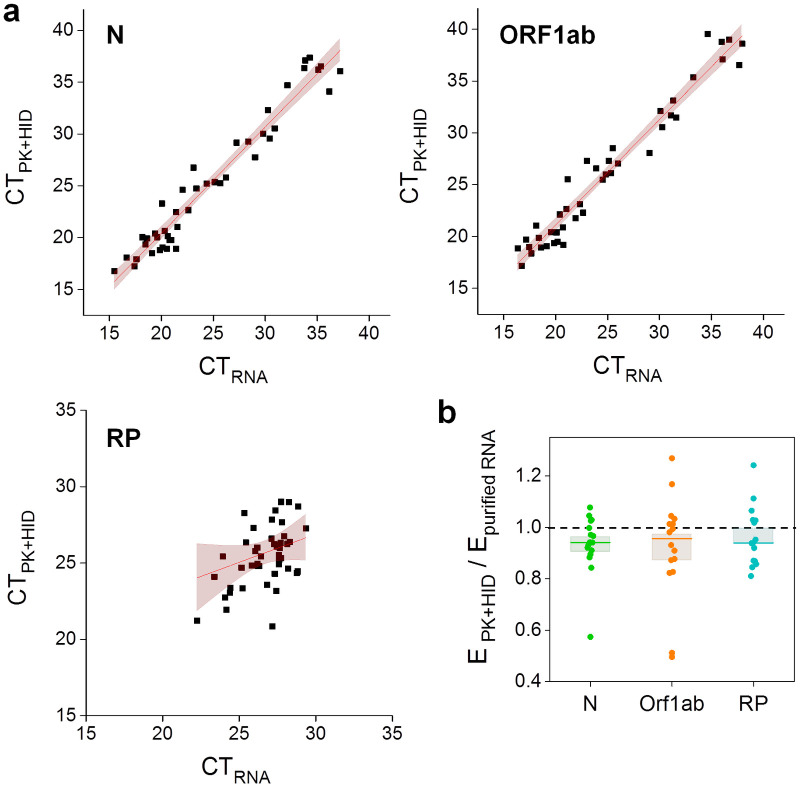
Fig 3. PK+HID method exhibits a similar performance than RNA extraction in RT-qPCR determinations of the SARS-CoV-2 N and ORF1ab genes.
Positive nasopharyngeal swab samples were processed for RNA extraction (purified RNA) or subjected to treatment with PK 1 mg/ml (55°C for 15 min) followed by heat-inactivation at 98°C for 5 min (PK+HID). The viral N and ORF1ab genes and the human RP gene were amplified and detected by RT-qPCR. (a) CT values obtained for the same samples prepared by the two different methods, the line obtained by regression of the data (continuous lines) and 95% confidence bands (pink) are represented. The parameter values obtained from the fitting were: slope = 1.02 ± 0.04 and intercept = 0.1 ± 0.9 (N amplicon); slope = 1.02 ± 0.04 and intercept = 0.8 ± 0.9 (ORF1ab amplicon) and slope = 0.4 ± 0.2 and intercept = 15 ± 6 (RP amplicon). Notice that CT values determined for RP spans a smaller range. (b) Amplification efficiencies obtained in PK+HID samples (EPK+HID) relative to the corresponding purified RNA samples (Epurified RNA). The mean values obtained for Epurified RNA were: 1.98 ± 0.03 (N), 2.02 ± 0.06 (ORF1ab) and 1.94 ± 0.03 (RP). The median of each measurement is represented with a line in the bars and the lengths of these bars represent the standard error (N = 16).