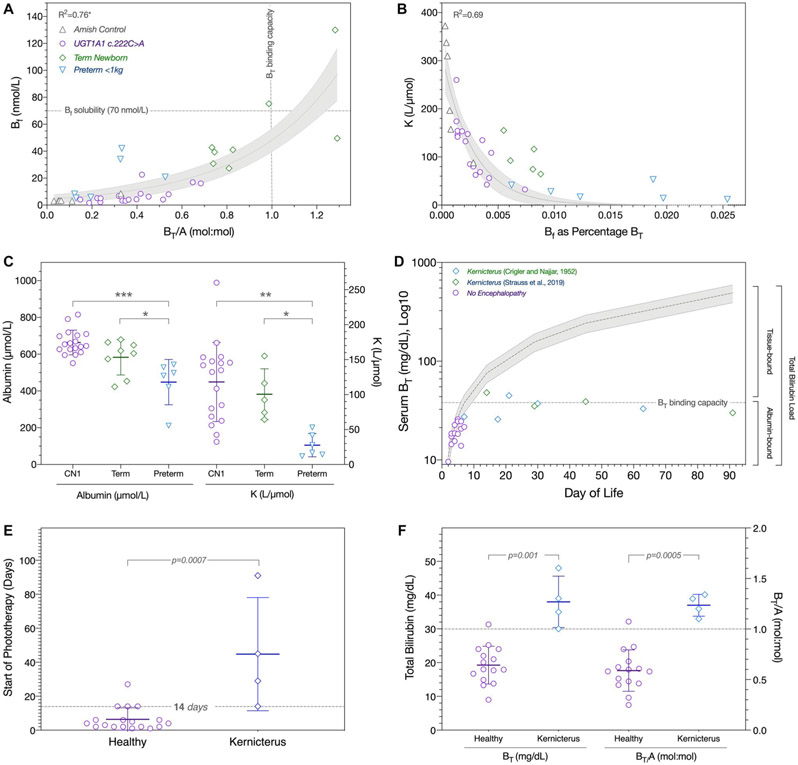
FIG. 2.
Bilirubin–albumin binding, tissue loading, and kernicterus. (A) Gray horizontal and vertical lines indicate Bf aqueous solubility and intravascular BT binding capacity, respectively. There is an exponential relationship between Bf and BT/A (R2 = 0.76; 95% confidence interval shaded gray) (Amish controls, gray triangles; UGTA1A c.222C>A homozygotes, purple circles; term newborns with idiopathic jaundice, green diamonds; preterm infants weighing less than 1 kg, blue triangles). (B) The proportion of BT represented by Bf decreases exponentially with increasing values of K (R2 = 0.69). (C) UGT1A1 c.222C>A homozygotes (CN1) as compared with jaundiced term newborns had similar albumin concentrations (left y-axis) and calculated values of K (right y-axis), whereas preterm babies weighing less than 1 kg had the lowest levels of both albumin and K (ANOVA P < 0.0001; Tukey’s post hoc test: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). (D) BT values (log10 scale) are plotted for 5 patients originally described by Crigler and Najjar (green diamonds(1)), 4 neonates from the present cohort who developed kernicterus (blue diamonds), and 14 UGT1A1 c.222C>A homozygotes who escaped neurological injury (purple circles). Gray shading depicts the theoretical increase of BT if produced at a steady rate of 3.7 ± 0.9 mg/kg per day and confined to the circulation. Within a normal range of albumin concentrations (3.5 and 4.5 g/dL), intravascular binding capacity (horizontal dashed line) saturates between 5 and 10 days of age and sets an upper limit on the concentration of intravascular BT. Thereafter, unmeasured pigment binds to brain and other extravascular tissues and comes to comprise 60%-90% of the total bilirubin load at the time of kernicterus. (E) Neonates who developed kernicterus (blue diamonds) started phototherapy at a median age of 37 postnatal days as compared with 4 postnatal days of age for those who remained healthy (purple circles); initiation of phototherapy at 14 or more postnatal days of age (gray line) increased the likelihood of brain injury 3.5 fold. (F) All 4 neonates who suffered brain injury had a BT/A greater than 1.0 mol:mol between 15 and 45 postnatal days of age. The presenting BT/A was about 60% lower among the 24 remaining infants who did not develop kernicterus. As predictors of kernicterus during the neonatal period, BT ≥ 30 mg/dL or BT/A ≥ 1.0 mol:mol had equal specificity (93.3%) and PPV (80.0%).