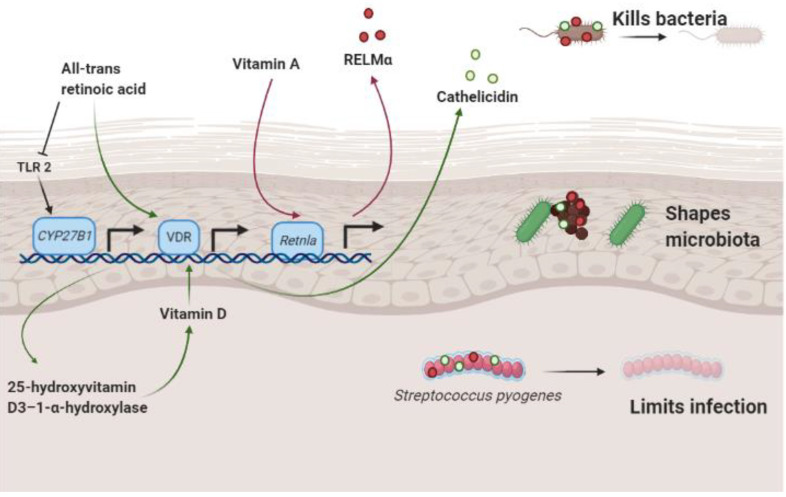
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of RELMα and cathelicidin involvement in skin immunity and the skin microbiome. Dietary vitamin A triggers the transcription of the Retnla gene which encodes the RELMα antimicrobial protein. When expressed, RELMα kills bacterial species that colonize the skin, shapes the resident microbiota and reduces the viability of invading pathogens such as Streptococcus pyogenes to limit infection. All-trans retinoic acid stimulates transcription of cathelicidin. When expressed, cathelicidin potentiates the immune response against microbial infection. Created in BioRender; adapted from Harris et al. [2]. RELMα, Resistin-like molecule α; Retnla, Resistin-like alpha precursor; CYP, cytochrome P450 family; VDR, Vitamin D receptor; TLR, toll-like receptor.