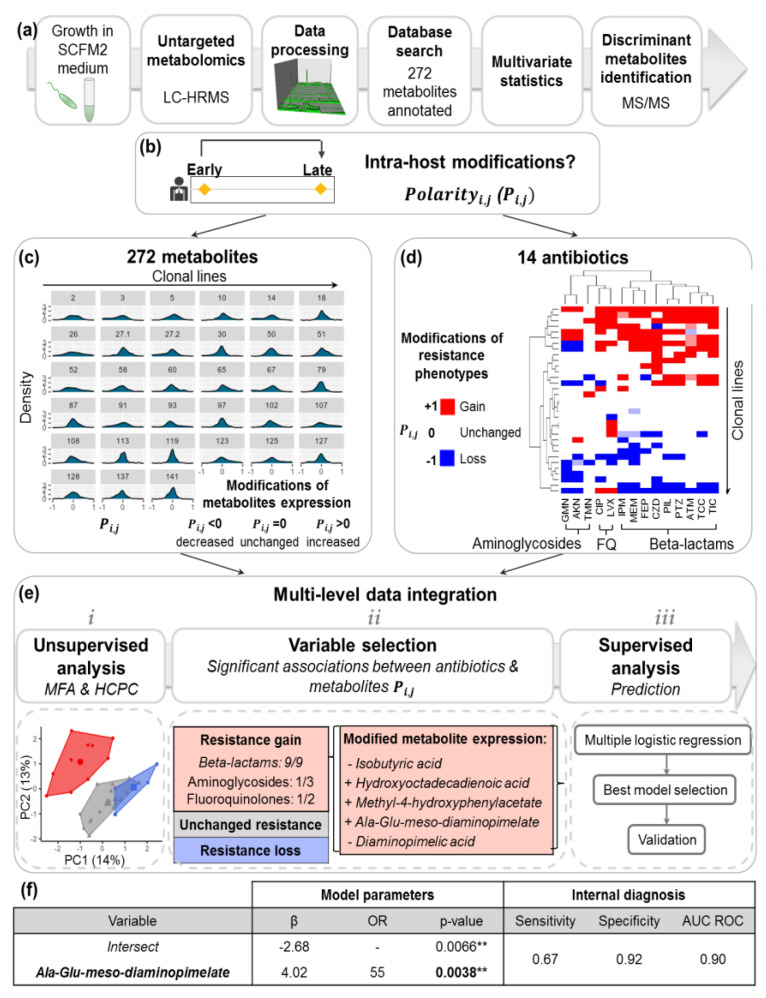
Figure 2.
Multiscale analysis identifies within-host metabolic modifications of P.a associated with the acquisition of beta-lactam resistances. (a) Schematic summary of untargeted LC-HRMS metabolomic analysis workflow for acquisition of P.a isolates’ metabolic profiles. (b) Intra-host modifications between early and late isolates from 33 evolutive lines have been assessed by calculating the Pi,j value for each line i, metabolite or resistance phenotype j. (c) Distributions of metabolite Pi,j representing intra-host modifications of 271 annotated metabolite intensities. (d) Hierarchical cluster analysis of antibiotic resistance Pi,j representing intra-host modifications of resistance against 14 antibiotics (*). (e) Multiscale data integration workflow for the identification of metabolic signatures associated with the acquisition of antibiotic resistance: (i) unsupervised HCPC identified 3 clusters of P.a lines with similar modifications of both antibiotic resistances and metabolite intensities; (ii) cluster 1 (in red) is significantly associated with acquisition of antibiotic resistances, especially against beta-lactams (χ2 p-value < 0.05), and with modifications in the abundance of 5 metabolites; (iii) selection of significantly associated metabolites and antibiotics to build a supervised logistic model predicting acquisition of antibiotic resistances from metabolic changes; (f) cross-validation of the best logistic regression model, which predicts the acquisition of beta-lactam resistance from an increased production of Ala-Glu-meso-diaminopimelate. ** p-values < 0.01. (*) abbreviations: FQ: fluoroquinolones; AKN: amikacin, ATM: aztreonam, CIP: ciprofloxacin, CZD: ceftazidime, FEP: cefepime, GMN: gentamicin, IPM: imipenem, LVX: levofloxacin, MEM: meropenem, PIL: piperacillin, PTZ: piperacillin-tazobactam, TCC: ticarcillin-clavulanic acid, TIC: ticarcillin, TMN: tobramycin.