Fig. 1. Characterization of DYBLUP from sperm flagella of the ascidian C. intestinalis.
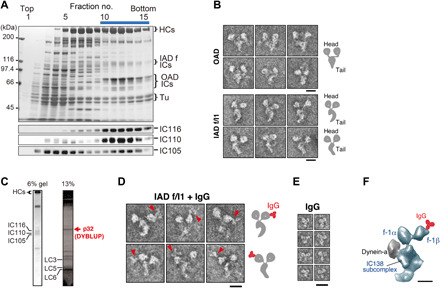
(A) Sucrose density gradient centrifugation of high salt/ATP extract from flagellar axonemes. Proteins separated in 6% SDS gels and corresponding Western blots using antibodies against orthologs of Chlamydomonas IC140 (IC116), IC138 (IC110), and IC97 (IC105) are shown. The bar represents the fractions subjected to Uno Q anion-exchange column chromatography (fig. S1B). (B) Electron micrographs of the negatively stained OAD and IAD f/I1 dynein. Both show two-headed structures but differ in the shape of their tails. Schematic drawings are shown on the right. Scale bars, 20 nm. (C) Subunit composition of Ciona f/I1 dynein. The 32-kDa protein DYBLUP is indicated in red. (D) Labeling of f/I1 dynein with anti-DYBLUP IgG. The images in the top and bottom rows correspond to two opposite orientations when the molecules are adsorbed to the carbon support film. The labeled motor domain is located on the convex side of the tail surface. Schematic drawings are shown on the right. Scale bar, 20 nm. (E) Images of IgG molecule. Scale bar, 20 nm. (F) Localization of DYBLUP on the 1β motor domain. The f/I1 dynein image extracted from the cryo-ET structure of an axoneme [EMD-5330; (18)] is oriented as in the top row of (D). Comparison with the IgG-labeled negative-stain images specifies the position of the label on the motor domain. Scale bar, 10 nm.
