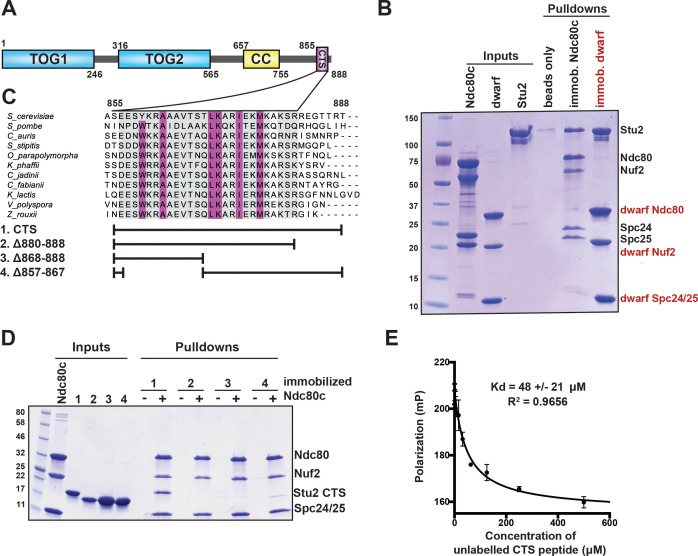
Figure 1. Binding of Stu2 C-terminal segment (CTS) with Ndc80c.
(A) Schematic representation of the domain structure of Stu2, showing the tubulin-binding TOG domains, the dimeric coiled-coil, and the CTS. Molecular mass markers shown indicate molecular weight in kDa. (B) Association of full-length Ndc80c and Stu2. Dwarf and full-length Ndc80c were immobilized to saturation on Ni-NTA agarose and incubated with Stu2. After extensive washing, bound proteins were eluted with buffer containing 400 mM imidazole. (C) Multiple sequence alignment showing conservation of the CTS among budding and fission yeasts. Conservation calculated using T-Coffee Server (gray boxes) and percent identity calculated using Clustal Omega (purple boxes). The bars below the alignment correspond to the Saccharomyces cerevisiae sequence in the alignment and show the constructs used in the pulldown experiments in (D). The blank parts of each line represent deletions. (D) Binding of Ndc80cdwarf and Stu2 CTS. The Stu2 constructs used in this experiment consist of the Stu2 coiled-coil domain, followed by a glycine-serine linker, followed by the regions of the CTS indicated by the bars in (C). Ndc80cdwarf was immobilized on Co-NTA agarose and incubated with Stu2. After extensive washing, bound proteins were eluted with buffer containing 400 mM imidazole. (E) Affinity of Ndc80cdwarf and Stu2 CTS. Competition fluorescence polarization, showing displacement of Oregon-green labeled CTS peptide (50 nM) from Ndc80cdwarf (10 µM) with increasing concentrations of an unlabeled CTS peptide. Polarization (in milliP) is plotted against concentration of unlabeled peptide. Data fitted with a single-site saturation binding model implemented in GraphPad Prism 9.