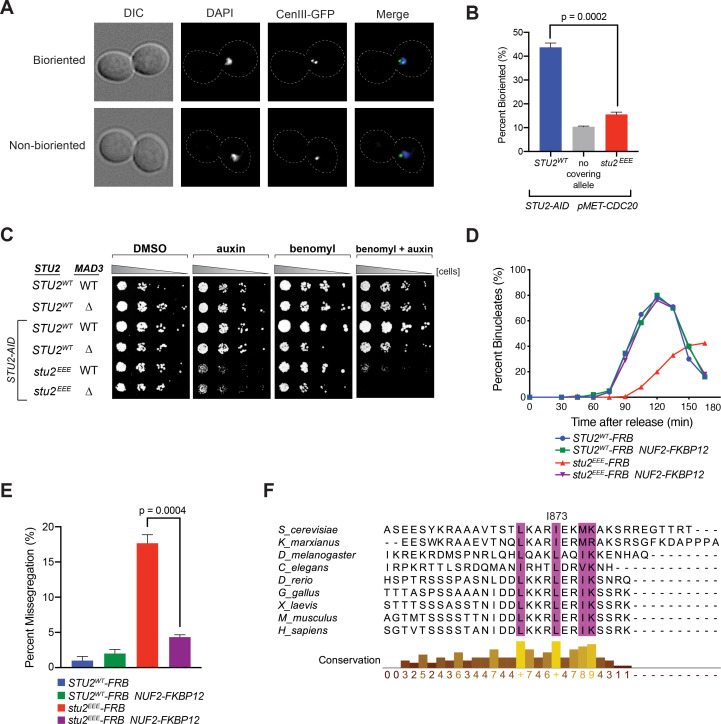
Figure 4. Cellular phenotypes of stu2EEE and conservation of key residues in multicellular eukaryotes.
(A) Exponentially growing STU2-AID pMET-CDC20 cultures with an ectopically expressed STU2 allele (STU2WT, M1154; stu2EEE, M1610) or no ectopic allele (no covering allele, M1153) and also containing CEN3 marked with GFP (CEN3::lacO LacI-GFP) were arrested in methionine + auxin containing media for 2.5 hr. Representative micrographs for bioriented and non-bioriented cells shown. (B) Percent bioriented cells were measured for cultures described in (A). Three replicates of n = 200 cells shown; p-value determined with unpaired t-test. (C) Wild-type cells (M3), cells with spindle checkpoint mutation (mad3Δ, M36), and STU2-AID cells expressing an ectopic copy of STU2 without and with a spindle checkpoint mutation (STU2WT, M622; STU2WT mad3Δ, M1622; stu2EEE, M1444; stu2EEE mad3Δ, M1541) were serially diluted (fivefold) and spotted on plates containing DMSO, 500 μM auxin, 5 μg/mL benomyl, or 500 μM auxin + 5 μg/mL benomyl. (D) STU2-AID cells expressing STU2-FRB alleles at an ectopic locus with NUF2 or NUF2-FKBP12 (STU2WT-FRB, M1513; stu2EEE-FRB, M1515; STU2WT-FRB NUF2-FKBP12, M1505; stu2EEE-FRB NUF2-FKBP12, M1507) were released from a G1 arrest into auxin and rapamycin containing media. Cell cycle progression determined by the accumulation of binucleate cells. (E) STU2-AID mad3∆ cells expressing STU2-FRB alleles at an ectopic locus with NUF2 or NUF2-FKBP12 (STU2WT-FRB, M2025; stu2EEE-FRB, M2024; STU2WT-FRB NUF2-FKBP12, M2027; stu2EEE-FRB NUF2-FKBP12, M2026) that also contained a fluorescently labeled centromere of chromosome III were released from G1 arrest into auxin- and rapamycin-containing medium. Quantification of chromosome mis-segregation in anaphase (percent of binucleate cells with a fluorescently labeled chromosome III signal in only one of the two nuclei). Shown is an average of three biological replicates, n = 100 cells each. (F) Multiple sequence alignment of the Stu2 C-terminus and C-termini from Stu2 eukaryotic homologs. Histogram shows conservation score generated with Clustal Omega. Highly conserved residues, including hydrophobic amino acids important for Ndc80c binding, are boxed in purple.
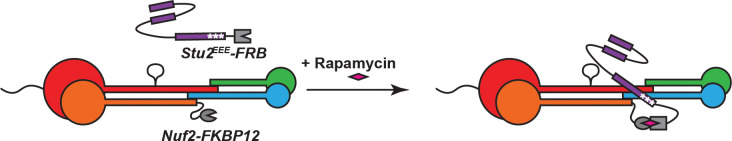
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Schematic illustrating re-tethering of Stu2EEE to Ndc80c.
Figure 4—figure supplement 2. Reproduction of western blot from Figure 3D also showing immunoblot signal for Dsn1-6His-3Flag.
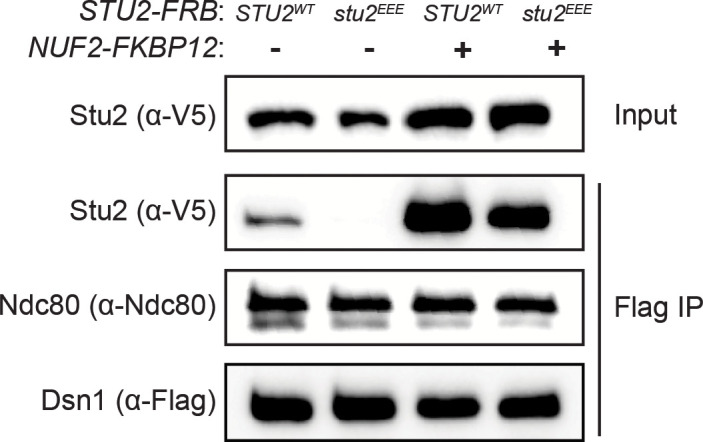
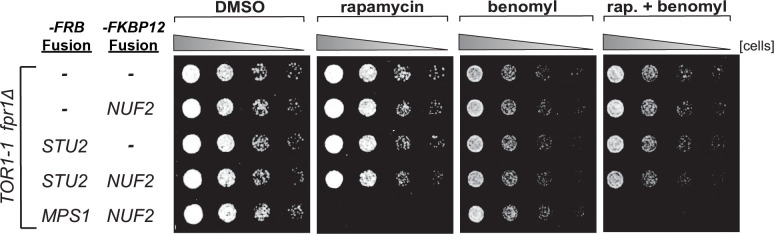
Figure 4—figure supplement 3. Characterization of STU2-FRB and NUF2-FKBP12 fusion alleles.
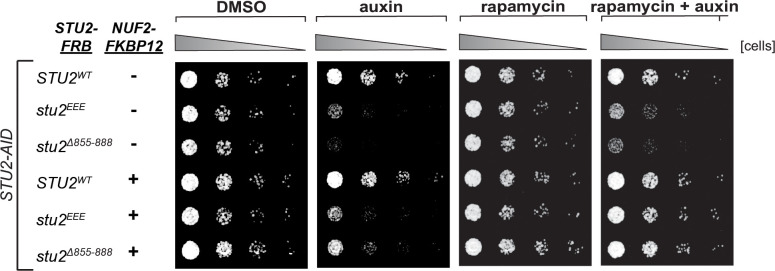
Figure 4—figure supplement 4. Tethering Stu2∆855-888-FRB to Ndc80c restores viability to the same degree as does tethering Stu2EEE-FRB.
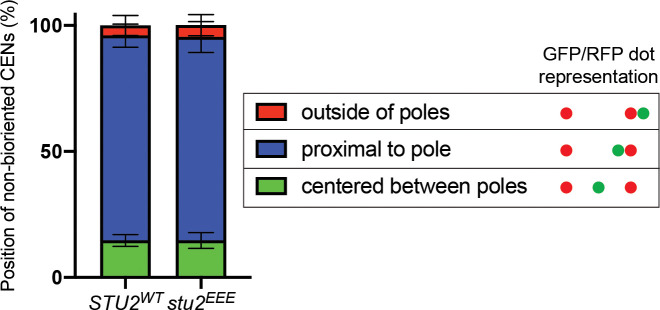
Figure 4—figure supplement 5. Examining the axial position of unseparated sister centromeres along the length of the mitotic spindle.
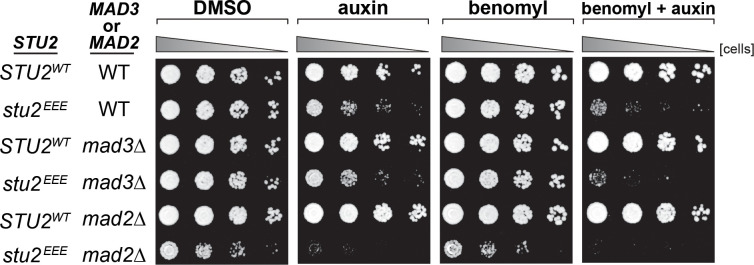
Figure 4—figure supplement 6. Synthetic growth defects of stu2EEE with mad2∆ and mad3∆.
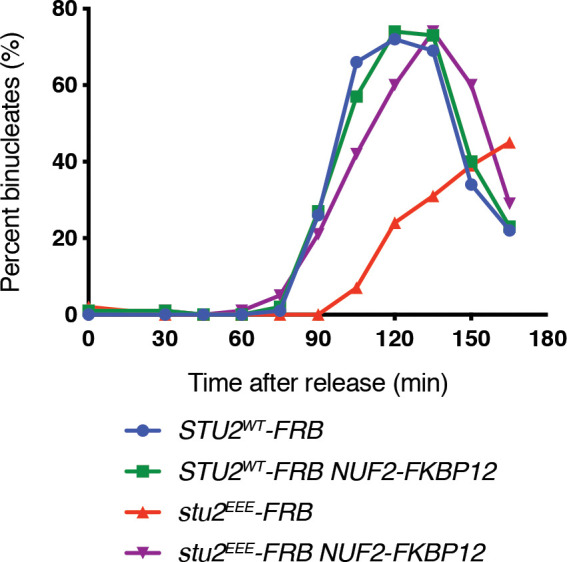
Figure 4—figure supplement 7. Replicate cell cycle delay experiment as described in Figure 4D.