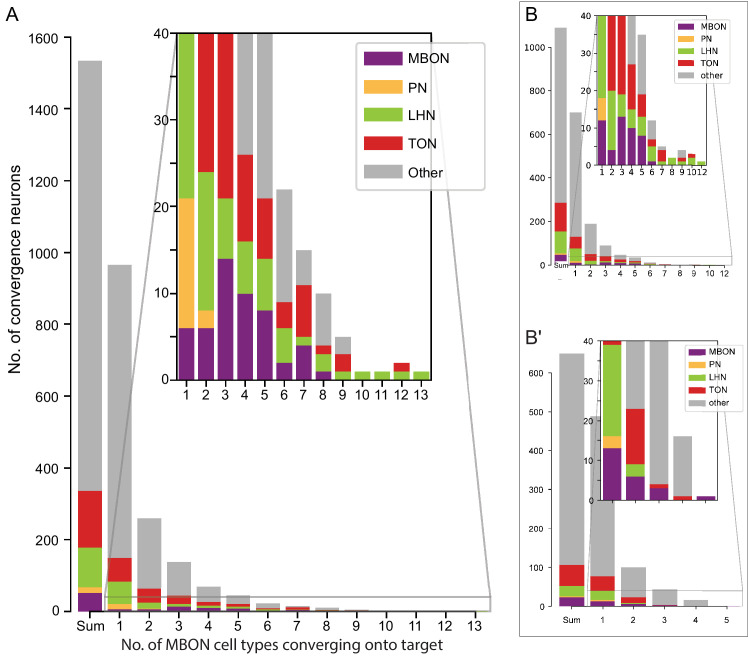
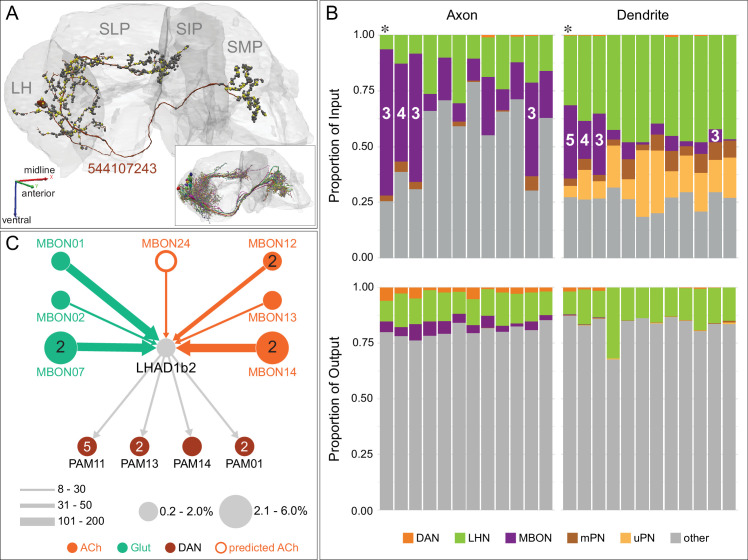
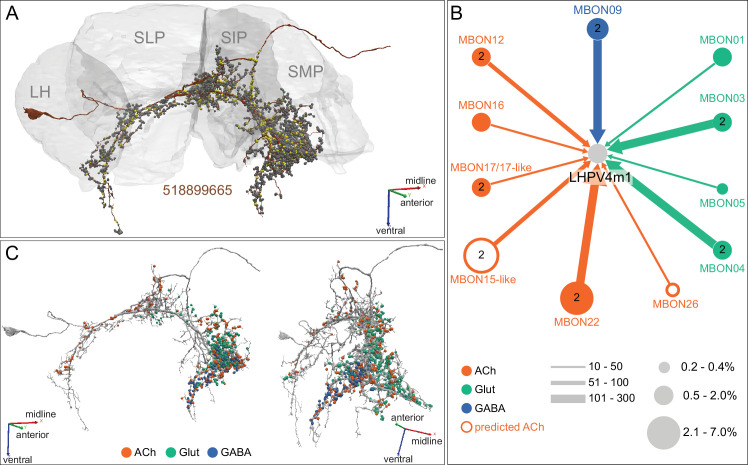
Figure 21. Downstream targets of MBONs often receive input from more than one MBON.
(A) About 1550 neurons are downstream (including axo-axonal connections) of one or more of the 34 MBON cell types when a threshold of 10 synapses is used. Among them, about 600 are downstream of at least 2 MBON cell types and are therefore capable of integrating information from multiple MBONs. The inset shows an expanded view of the indicated portion of the plot. These neurons include a range of well-characterized neuron types, including MBONs, olfactory projection neurons (PNs), lateral horn neurons (LHNs), and third-order olfactory neurons (TONs; downstream targets of PNs outside the LH, see Schlegel et al., 2020) as well as less characterized neurons (other). Among the neurons that receive input from 10 or more MBON types, LHNs are heavily over-represented. (B-B′) The distribution shown in (A) has been divided into two separate histograms, one showing neurons downstream of multiple typical MBONs, in which atypical MBONs have not been counted (B), and one showing neurons downstream of multiple atypical MBONs, in which typical MBONs have not been counted (B′). The insets show expanded views of the indicated portions of each plot. Atypical MBONs show less convergence than the typical MBONs and do not preferentially converge onto LHNs.